A semantics, energy-based approach to automate biomodel composition
- PMID: 35657966
- PMCID: PMC9165793
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269497
A semantics, energy-based approach to automate biomodel composition
Abstract
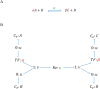
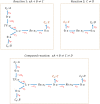
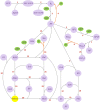
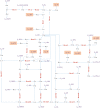
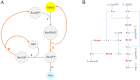
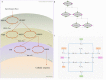
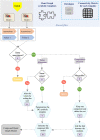
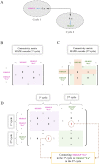
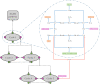
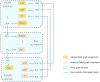
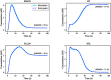
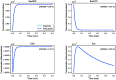
Hierarchical modelling is essential to achieving complex, large-scale models. However, not all modelling schemes support hierarchical composition, and correctly mapping points of connection between models requires comprehensive knowledge of each model's components and assumptions. To address these challenges in integrating biosimulation models, we propose an approach to automatically and confidently compose biosimulation models. The approach uses bond graphs to combine aspects of physical and thermodynamics-based modelling with biological semantics. We improved on existing approaches by using semantic annotations to automate the recognition of common components. The approach is illustrated by coupling a model of the Ras-MAPK cascade to a model of the upstream activation of EGFR. Through this methodology, we aim to assist researchers and modellers in readily having access to more comprehensive biological systems models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
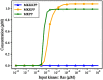
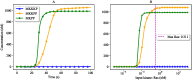
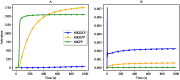
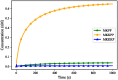
References
-
- Le Novere N, Bornstein B, Broicher A, Courtot M, Donizelli M, Dharuri H, et al. BioModels Database: a free, centralized database of curated, published, quantitative kinetic models of biochemical and cellular systems. Nucleic acids research. 2006;34(suppl_1):D689–D691. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

