Phase II Randomized Study of Ramucirumab and Pembrolizumab Versus Standard of Care in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Immunotherapy-Lung-MAP S1800A
- PMID: 35658002
- PMCID: PMC9287284
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.00912
Phase II Randomized Study of Ramucirumab and Pembrolizumab Versus Standard of Care in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Immunotherapy-Lung-MAP S1800A
Erratum in
-
Erratum.J Clin Oncol. 2022 Sep 1;40(25):3002. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01464. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36037534 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents a major unmet need. Combining ICI with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor inhibition has yielded promising results in multiple tumor types.
Methods: In this randomized phase II Lung-MAP nonmatch substudy (S1800A), patients ineligible for a biomarker-matched substudy with NSCLC previously treated with ICI and platinum-based chemotherapy and progressive disease at least 84 days after initiation of ICI were randomly assigned to receive ramucirumab plus pembrolizumab (RP) or investigator's choice standard of care (SOC: docetaxel/ramucirumab, docetaxel, gemcitabine, and pemetrexed). With a goal of 130 eligible patients, the primary objective was to compare overall survival (OS) using a one-sided 10% level using the better of a standard log-rank (SLR) and weighted log-rank (WLR; G[rho = 0, gamma = 1]) test. Secondary end points included objective response, duration of response, investigator-assessed progression-free survival, and toxicity.
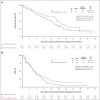
Results: Of 166 patients enrolled, 136 were eligible (69 RP; 67 SOC). OS was significantly improved with RP (hazard ratio [80% CI]: 0.69 [0.51 to 0.92]; SLR one-sided P = .05; WLR one-sided P = .15). The median (80% CI) OS was 14.5 (13.9 to 16.1) months for RP and 11.6 (9.9 to 13.0) months for SOC. OS benefit for RP was seen in most subgroups. Investigator-assessed progression-free survival (hazard ratio [80% CI]: 0.86 [0.66 to 1.14]; one-sided SLR, P = .25 and .14 for WLR) and response rates (22% RP v 28% SOC, one-sided P = .19) were similar between arms. Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 42% of patients in the RP group and 60% on SOC.
Conclusion: This randomized phase II trial demonstrated significantly improved OS with RP compared with SOC in patients with advanced NSCLC previously treated with ICI and chemotherapy. The safety was consistent with known toxicities of both drugs. These data warrant further evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

Comment in
-
Lung-MAP: A Collaborative Roadmap to Improve Cancer Outcomes.J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jul 20;40(21):2285-2287. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01035. Epub 2022 Jun 3. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35658027 No abstract available.
References
-
- Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, et al. : Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 29:iv192-iv237, 2018. (suppl 4) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

