TP53 Sequencing and p53 Immunohistochemistry Predict Outcomes When Bevacizumab Is Added to Frontline Chemotherapy in Endometrial Cancer: An NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study
- PMID: 35658479
- PMCID: PMC9553389
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.02506
TP53 Sequencing and p53 Immunohistochemistry Predict Outcomes When Bevacizumab Is Added to Frontline Chemotherapy in Endometrial Cancer: An NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study
Abstract
Purpose: The status of p53 in a tumor can be inferred by next-generation sequencing (NGS) or by immunohistochemistry (IHC). We examined the association between p53 IHC and sequence and whether p53 IHC alone, or integrated with TP53 NGS, predicts the outcome.
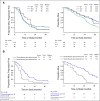
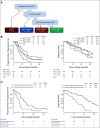
Methods: From GOG-86P, a randomized phase II study of chemotherapy combined with either bevacizumab or temsirolimus in advanced endometrial cancer, 213 cases had p53 protein expression data measured by IHC and TP53 NGS data. An analysis was designed to integrate p53 expression by IHC with the presence or absence of a TP53 mutation. These variables were further correlated with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the chemotherapy plus bevacizumab arms versus the chemotherapy plus temsirolimus arm.
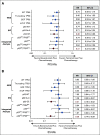
Results: In the analysis of p53 IHC, the most striking treatment effect favoring bevacizumab was in cases where p53 was overexpressed (PFS hazard ratio [HR]: 0.46, 95% CI, 0.26 to 0.88; OS HR: 0.31, 95% CI, 0.16 to 0.62). On integrated analysis, patients with TP53 missense mutations and p53 protein overexpression had a similar treatment effect on PFS (HR: 0.41, 95% CI, 0.22 to 0.83) and OS (HR: 0.28, 95% CI, 0.14 to 0.59) favoring bevacizumab plus chemotherapy relative to temsirolimus plus chemotherapy. Concordance between TP53 NGS and p53 IHC was 88%. Concordance was 92% when cases with TP53 mutations and POLE mutations or mismatch repair deficiency were removed.
Conclusion: IHC for p53 alone or when integrated with sequencing for TP53 identifies a specific, high-risk tumor genotype/phenotype for which bevacizumab is particularly beneficial in improving outcomes when combined with chemotherapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00977574.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


Comment in
-
TP53 Gene Indels Impact on Cancer Outcomes.J Clin Oncol. 2023 Jan 1;41(1):145-147. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.01385. Epub 2022 Sep 16. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36112962 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2022, Atlanta, GA, American Cancer Society, 2022
-
- Sheikh MA, Althouse AD, Freese KE, et al. : USA endometrial cancer projections to 2030: Should we be concerned? Future Oncol 10:2561-2568, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. : Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209-249, 2021 - PubMed
-
- Cancer Facts and Figures 2020, Atlanta, GA, American Cancer Society, 2020
-
- Ferlay J, Laversanne M, Ervik M, et al. : Global Cancer Observatory. Lyon, France, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

