Toxoplasma gondii Infection Decreases Intestinal 5-Lipoxygenase Expression, while Exogenous LTB4 Controls Parasite Growth
- PMID: 35658510
- PMCID: PMC9302167
- DOI: 10.1128/iai.00029-22
Toxoplasma gondii Infection Decreases Intestinal 5-Lipoxygenase Expression, while Exogenous LTB4 Controls Parasite Growth
Abstract
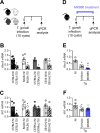
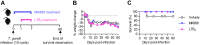
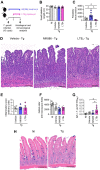
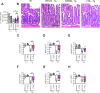
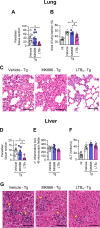
5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) is an enzyme required for the production of leukotrienes and lipoxins and interferes with parasitic infections. In vitro, Toxoplasma gondii inhibits leukotriene B4 (LTB4) production, and mice deficient in 5-LO are highly susceptible to infection. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of the pharmacological inhibition of the 5-LO pathway and exogenous LTB4 supplementation during experimental toxoplasmosis. For this purpose, susceptible C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with T. gondii and treated with LTB4 or MK886 (a selective leukotriene inhibitor through inhibition of 5-LO-activating protein [FLAP]). The parasitism, histology, and immunological parameters were analyzed. The infection decreased 5-LO expression in the small intestine, and treatment with MK886 reinforced this reduction during infection; in addition, MK886-treated infected mice presented higher intestinal parasitism, which was associated with lower local interleukin-6 (IL-6), interferon gamma (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) production. In contrast, treatment with LTB4 controlled parasite replication in the small intestine, liver, and lung and decreased pulmonary pathology. Interestingly, treatment with LTB4 also preserved the number of Paneth cells and increased α-defensins expression and IgA levels in the small intestine of infected mice. Altogether, these data demonstrated that T. gondii infection is associated with a decrease in 5-LO expression, and on the other hand, treatment with the 5-LO pathway product LTB4 resulted in better control of parasite growth in the organs, adding to the knowledge about the pathogenesis of T. gondii infection.
Keywords: Paneth cells; antimicrobial peptides; eicosanoids; experimental toxoplasmosis; intestinal immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma gondii alters eicosanoid release by human mononuclear phagocytes: role of leukotrienes in interferon gamma-induced antitoxoplasma activity.J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1637-48. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1637. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 7964451 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandins inhibit 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein expression and leukotriene B4 production from dendritic cells via an IL-10-dependent mechanism.J Immunol. 2003 Jan 1;170(1):139-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.139. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12496393
-
Parasite-induced lipoxin A4 is an endogenous regulator of IL-12 production and immunopathology in Toxoplasma gondii infection.J Exp Med. 2002 Nov 4;196(9):1253-62. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021183. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12417634 Free PMC article.
-
[Rudolf-Virchow Prize 1998. Award lecture. Toxoplasmosis: a model infection for studying systemic and intracerebral immune reactions].Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998;82:9-22. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998. PMID: 10095413 German.
-
Contrasting effects of proinflammatory and T-helper lymphocyte subset-2 cytokines on the 5-lipoxygenase pathway in monocytes.Kidney Int. 1997 May;51(5):1520-8. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.209. Kidney Int. 1997. PMID: 9150468
Cited by
-
Leukotrienes in Innate Immunity: Still Underappreciated after All These Years?J Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;210(3):221-227. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200599. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36649580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory response and parasite regulation in acute toxoplasmosis: the role of P2X7 receptor in controlling virulent atypical genotype strain of Toxoplasma gondii.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1452828. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1452828. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39267751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller DK, Gillard JW, Vickers PJ, Sadowski S, Léveillé C, Mancini JA, Charleson P, Dixon RAF, Ford-Hutchinson AW, Fortin R, Gauthier JY, Rodkey J, Rosen R, Rouzer C, Sigal IS, Strader CD, Evans JF. 1990. Identification and isolation of a membrane protein necessary for leukotriene production. Nature 343:278–281. 10.1038/343278a0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

