Treatment of posterior circulation stroke: Acute management and secondary prevention
- PMID: 35658624
- PMCID: PMC9358302
- DOI: 10.1177/17474930221107500
Treatment of posterior circulation stroke: Acute management and secondary prevention
Abstract
One-fifth of strokes occur in the territory of the posterior circulation, but their management, particularly acute reperfusion therapy and neurointervention procedures for secondary prevention, has received much less attention than similar interventions for the anterior circulation. In this review, we overview the treatment of posterior circulation stroke, including both interventions in the acute setting and secondary prevention. We focus on areas in which the management of posterior circulation stroke differs from that of stroke in general and highlight recent advances.Effectiveness of acute revascularization of posterior circulation strokes remains in large parts unproven. Thrombolysis seems to have similar benefits and lower hemorrhage risks than in the anterior circulation. The recent ATTENTION and BAOCHE trials have demonstrated that thrombectomy benefits strokes with basilar artery occlusion, but its effect on other posterior occlusion sites remains uncertain. Ischemic and hemorrhagic space-occupying cerebellar strokes can benefit from decompressive craniectomy.Secondary prevention of posterior circulation strokes includes aggressive treatment of cerebrovascular risk factors with both drugs and lifestyle interventions and short-term dual anti-platelet therapy. Randomized controlled trial (RCT) data suggest basilar artery stenosis is better treated with medical therapy than stenting, which has a high peri-procedural risk. Limited data from RCTs in stenting for vertebral stenosis suggest that intracranial stenosis is currently best treated with medical therapy alone; the situation for extracranial stenosis is less clear where stenting for symptomatic stenosis is an option, particularly for recurrent symptoms; larger RCTs are required in this area.
Keywords: Vertebral; acute stroke therapy; basilar; posterior circulation; prevention; stenting; treatment; vertebrobasilar.
Conflict of interest statement
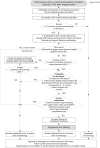
Figures





References
-
- Feigin VL, Brainin M, Norrving B, et al. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int J Stroke 2022; 17: 18–29. - PubMed
-
- Markus HS, van der Worp HB, Rothwell PM. Posterior circulation ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack: diagnosis, investigation, and secondary prevention. Lancet Neurol 2013; 12: 989–998. - PubMed
-
- Lindley RI, Wardlaw JM, Whiteley WN, et al. Alteplase for acute ischemic stroke: outcomes by clinically important subgroups in the Third International Stroke Trial. Stroke 2015; 46: 746–756. - PubMed
-
- Keselman B, Gdovinová Z, Jatuzis D, et al. Safety and outcomes of intravenous thrombolysis in posterior versus anterior circulation stroke: results from the safe implementation of treatments in stroke registry and meta-analysis. Stroke 2020; 51: 876–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

