Development of sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for COVID-19 diagnosis by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein detection based on Au@BSA-luminol nanocomposites
- PMID: 35659688
- PMCID: PMC9130314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2022.108161
Development of sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for COVID-19 diagnosis by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein detection based on Au@BSA-luminol nanocomposites
Abstract
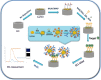
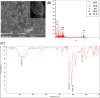
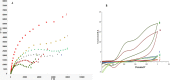
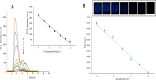
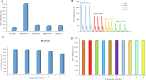
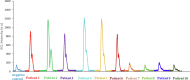
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a new and highly contagious disease posing a threat to global public health and wreaking havoc around the world. It's caused by the Coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2). In the current pandemic situation, rapid and accurate SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis on a large scale is critical for early-stage diagnosis. Early detection and monitoring of viral infections can aid in controlling and preventing infection in large groups of people. Accordingly, we developed a sensitive and high-throughput sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on antigen detection for COVID-19 diagnosis (the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2). For the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, the ECL biosensor had a linear range of 10 ng mL-1 to 10 µg mL-1 with a limit of detection of 1.93 ng mL-1. The sandwich ECL immunosensor could be used in early clinical diagnosis due to its excellent recovery in detecting SARS-CoV-2, rapid analysis (90 min), and ease of use.
Keywords: Au@BSA-luminol; COVID-19; Electrochemiluminescence; SARS-CoV-2; Sandwich immunosensor.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sandwich-format ECL immunosensor based on Au star@BSA-Luminol nanocomposites for determination of human chorionic gonadotropin.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Mar 15;101:219-226. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.10.040. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29096359
-
Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using Electrochemical Immunosensor.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jan 8;21(2):390. doi: 10.3390/s21020390. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33429915 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical immunosensor with Cu2O nanocube coating for detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Mar 2;188(3):105. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04762-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 33651173 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 using potential point-of-care electrochemical immunosensor: Toward the future prospects.Int Rev Immunol. 2021;40(1-2):126-142. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1872566. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Int Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33448909 Review.
-
Diagnosis of COVID-19 for controlling the pandemic: A review of the state-of-the-art.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Feb 15;174:112830. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112830. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33339696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRET-based immunoassay on magnetic beads for selective and sensitive detection of Nanog antigen as a key cancer stem cell marker.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Jun 25;191(7):419. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06505-y. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38916771
-
Aptamer Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;25(6):1637. doi: 10.3390/s25061637. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40292706 Free PMC article.
-
Recent trends and advancements in electrochemiluminescence biosensors for human virus detection.Trends Analyt Chem. 2022 Dec;157:116727. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2022.116727. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Trends Analyt Chem. 2022. PMID: 35815064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double-antibody-based nano-biosensing system for the onsite monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 variants.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2023 Aug 21;9:105. doi: 10.1038/s41378-023-00578-0. eCollection 2023. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2023. PMID: 37614970 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on the Biofunctionalization of Gold Nanoparticles for the Rapid and Sensitive Multiplatform Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Its Proteins: From Computational Models to Validation in Human Samples.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 25;24(11):9249. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119249. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sánchez-Báscones E., Parra F., Lobo-Castañón M.J. Aptamers against viruses: selection strategies and bioanalytical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021;143:116349.
-
- Sobhanie E., Faridbod F., Hosseini M., Ganjali M. An Ultrasensitive ECL Sensor Based on Conducting Polymer/Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide for Non-Enzymatic Detection in Biological Samples. ChemistrySelect. 2020;5(17):5330–5336.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

