MiR-26a-tetrahedral framework nucleic acids mediated osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 35661456
- PMCID: PMC9251048
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13272
MiR-26a-tetrahedral framework nucleic acids mediated osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
Objectives: Delivery systems that provide time and space control have a good application prospect in tissue regeneration applications, as they can effectively improve the process of wound healing and tissue repair. In our experiments, we constructed a novel micro-RNA delivery system by linking framework nucleic acid nanomaterials to micro-RNAs to promote osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
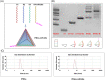
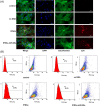
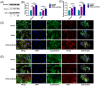
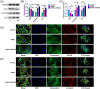
Materials and methods: To verify the successful preparation of tFNAs-miR-26a, the size of tFNAs-miR-26a were observed by non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and dynamic light scattering techniques. The expression of osteogenic differentiation-related genes and proteins was investigated by confocal microscope, PCR and western blot to detect the impact of tFNAs-miR-26a on ADSCs. And finally, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway related proteins and genes were detected by confocal microscope, PCR and western blot to study the relevant mechanism.
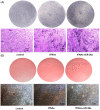
Results: By adding this novel complex, the osteogenic differentiation ability of mesenchymal stem cells was significantly improved, and the expression of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) on the surface of the cell membrane and the formation of calcium nodules in mesenchymal stem cells were significantly increased on days 7 and 14 of induction of osteogenic differentiation, respectively. Gene and protein expression levels of ALP (an early marker associated with osteogenic differentiation), RUNX2 (a metaphase marker), and OPN (a late marker) were significantly increased. We also studied the relevant mechanism of action and found that the novel nucleic acid complex promoted osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by activating the canonical Wnt signaling pathway.
Conclusions: This study may provide a new research direction for the application of novel nucleic acid nanomaterials in bone tissue regeneration.
© 2022 The Authors. Cell Proliferation published by European Cell Proliferation Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Xu XH, Yuan TJ, Dad HA, et al. Plant exosomes as novel nanoplatforms for microRNA transfer stimulate neural differentiation of stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Nano Lett. 2021;21:8151‐8159. - PubMed
-
- Li B. MicroRNA regulation in osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells and its application in bone regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13:26‐30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82100984/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970916/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- RCDWJS2021-20/Research Funding from West China School/Hospital of Stomatology Sichuan University
- 2022JDTD0021/Sichuan Province Youth Science and Technology Innovation Team
- 2019YFA0110600/National Key R&D Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

