Low-dose metformin and PEN2-dependent lysosomal AMPK activation: benefits outnumber side effects
- PMID: 35661690
- PMCID: PMC9166162
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-01040-9
Low-dose metformin and PEN2-dependent lysosomal AMPK activation: benefits outnumber side effects
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
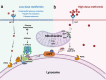
Comment on
-
Low-dose metformin targets the lysosomal AMPK pathway through PEN2.Nature. 2022 Mar;603(7899):159-165. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04431-8. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35197629 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

