Anti-MDA5 dermatomyositis after COVID-19 vaccination: a case-based review
- PMID: 35661906
- PMCID: PMC9166182
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-022-05149-6
Anti-MDA5 dermatomyositis after COVID-19 vaccination: a case-based review
Abstract
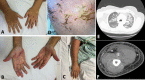
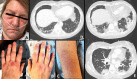
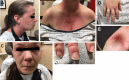
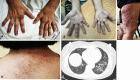
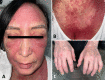
Anti-MDA5 (Melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5) myositis is a rare subtype of dermatomyositis (DM) characterized by distinct ulcerative, erythematous cutaneous lesions and a high risk of rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD). It has been shown that SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) replicates rapidly in lung and skin epithelial cells, which is sensed by the cytosolic RNA-sensor MDA5. MDA5 then triggers type 1 interferon (IFN) production, and thus downstream inflammatory mediators (EMBO J 40(15):e107826, 2021); (J Virol, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00862-21 ); (Cell Rep 34(2):108628, 2021); (Sci Rep 11(1):13638, 2021); (Trends Microbiol 27(1):75-85, 2019). It has also been shown that MDA5 is triggered by the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine with resultant activated dendritic cells (Nat Rev Immunol 21(4):195-197, 2021). Our literature review identified one reported case of MDA5-DM from the COVID-19 vaccine (Chest J, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2021.07.646 ). We present six additional cases of MDA5-DM that developed shortly after the administration of different kinds of COVID-19 vaccines. A review of other similar cases of myositis developing from the COVID-19 vaccine was also done. We aim to explore and discuss the evidence around recent speculations of a possible relation of MDA5-DM to COVID-19 infection and vaccine. The importance of vaccination during a worldwide pandemic should be maintained and our findings are not intended to discourage individuals from receiving the COVID-19 vaccine.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Dermatomyositis; MDA5.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
All co-authors are familiar with the revised, final version of the work and take full responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work. No part of the manuscript, including photographs, has been copied or published elsewhere.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Y, Du G, Zhang G, Matucci-Cerinic M, Furst DE. Similarities and differences between severe COVID-19 pneumonia and anti-MDA-5-positive dermatomyositis-associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung diseases: a challenge for the future, (in eng) Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218594. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

