The significance of surface neutrophilic MPO expression level in NETosis and NETosis-associated coagulopathies in covid-19 infected patients
- PMID: 35661911
- PMCID: PMC9148269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2022.102676
The significance of surface neutrophilic MPO expression level in NETosis and NETosis-associated coagulopathies in covid-19 infected patients
Abstract
Introduction: Inflammatory response-induced coagulopathy is a common complication associated with severe form of covid-19 infection. Evidences suggest that neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) play a significant role in triggering the immunothrombosis in this condition. We aimed to evaluate the diagnostic value of surface neutrophilic myeloperoxidase (MPO) as NETosis biomarker for predicting the risk of covid-19-associated coagulopathies.
Methods: Covid-19 infection was assessed by real-time-PCR and plasma d-dimer levels were measured by ELFA. Based on the covid-19 infection and d-dimer level outcomes, patients were categorized into four groups. Any alteration in the serum level of IL-6, H3Cit and neutrophilic surface MPO were analyzed by CLIA, ELISA, and flow cytometry, respectively.
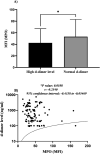
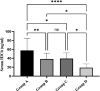
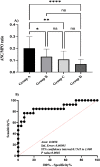
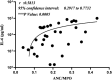
Results: H3Cit variations and different d-dimer values confirmed the association between NETosis and coagulopathies. Findings showed that the expression of neutrophilic MPO reduced in cases with NETosis, which was correlated with increased levels of H3Cit. ANC/MPO ratio was signified as a valuable marker to discriminate the covid-19 and non covid-19-associated coagulopathies and could be considered as a prognostic factor due to its noteworthy correlation with serum IL-6 concentration.
Conclusion: Declined levels of surface neutrophilic MPO in NETosis correlate with covid-19-associated coagulopathies and increased IL-6 levels, as a potential biomarker of covid-19 disease severity.
Keywords: Coagulopathies; NETosis; Surface myeloperoxidase.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Role of NETosis and Complement Activation in COVID-19-Associated Coagulopathies.Biomedicines. 2023 May 5;11(5):1371. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051371. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239041 Free PMC article.
-
Increased serum citrullinated histone H3 levels in COVID-19 patients with acute ischemic stroke.Ideggyogy Sz. 2022 May 30;75(5-06):191-198. doi: 10.18071/isz.75.0191. Ideggyogy Sz. 2022. PMID: 35819341 English.
-
NETosis induction reflects COVID-19 severity and long COVID: insights from a 2-center patient cohort study in Israel.J Thromb Haemost. 2023 Sep;21(9):2569-2584. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2023.02.033. Epub 2023 Apr 11. J Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 37054916 Free PMC article.
-
NETosis and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in COVID-19: Immunothrombosis and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 2;13:838011. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838011. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NETosis markers: Quest for specific, objective, and quantitative markers.Clin Chim Acta. 2016 Aug 1;459:89-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2016.05.029. Epub 2016 May 31. Clin Chim Acta. 2016. PMID: 27259468 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Release following Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Newborn Rats Treated with Therapeutic Hypothermia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3598. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043598. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835009 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of NETosis and Complement Activation in COVID-19-Associated Coagulopathies.Biomedicines. 2023 May 5;11(5):1371. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051371. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239041 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Neutrophil-Derived Myeloperoxidase (MPO) in Diseases: The New Progress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;13(1):132. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010132. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guan W., Ni Z., Hu Y., Liang W., Ou C., He J., et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. Vol. 382. Massachusetts Medical Society; 2020. pp. 1708–1720.101056/NEJMoa2002032 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

