Comparative Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatments for Adults With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 35662736
- PMCID: PMC9158498
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.885457
Comparative Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatments for Adults With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
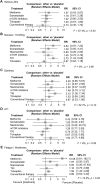
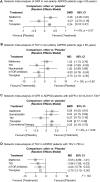
Background: Tolvaptan is the gold standard treatment for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), while several other drugs have the potential to inhibit the progression of ADPKD. However, individual clinical trials may not show sufficient differences in clinical efficacy due to small sample sizes. Furthermore, the differences in therapeutic efficacy among drugs are unclear. Herein, we investigated the effect of the ADPKD treatments. Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Medline, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library through January 2022 to identify randomized controlled trials in ADPKD patients that compared the effects of treatments with placebo or conventional therapy. A network meta-analysis was performed to compare the treatments indirectly. The primary outcomes were changes in kidney function and the rate of total kidney volume (TKV) growth. Results: Sixteen studies were selected with a total of 4,391 patients. Tolvaptan significantly preserved kidney function and inhibited TKV growth compared to the placebo {standardized mean difference (SMD) [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 0.24 (0.16; 0.31) and MD: -2.70 (-3.10; -2.30), respectively}. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors inhibited TKV growth compared to the placebo; somatostatin analogs significantly inhibited TKV growth compared to the placebo and tolvaptan [MD: -5.69 (-7.34; -4.03) and MD: -2.99 (-4.69; -1.29), respectively]. Metformin tended to preserve renal function, although it was not significant [SMD: 0.28 (-0.05; 0.61), p = 0.09]. Conclusion: The therapeutic effect of tolvaptan was reasonable as the gold standard for ADPKD treatment, while somatostatin analogs also showed notable efficacy in inhibiting TKV growth. Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42022300814.
Keywords: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; kidney function; network meta-analysis; tolvaptan; total kidney volume.
Copyright © 2022 Tsukamoto, Urate, Yamada, Azushima, Yamaji, Kinguchi, Uneda, Kanaoka, Wakui and Tamura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
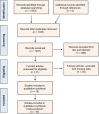
Figures


References
-
- Caroli A., Perico N., Perna A., Antiga L., Brambilla P., Pisani A., et al. (2013). Effect of Longacting Somatostatin Analogue on Kidney and Cyst Growth in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ALADIN): a Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre Trial. Lancet 382, 1485–1495. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61407-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

