Sleep quality and anxiety among Egyptian population during covid-19 pandemic
- PMID: 35662958
- PMCID: PMC9153968
- DOI: 10.5935/1984-0063.20210020
Sleep quality and anxiety among Egyptian population during covid-19 pandemic
Abstract
Objectives: COVID-19 pandemic imposed a relevant number of stressful factors potentially impacting either daytime function or sleep quality. This study aimed to assess the sleep quality and anxiety among the general population living in Egypt.
Material and methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 1,000 individuals who have been recruited via a convenience sample. A predesigned questionnaire was distributed online to collect data on sleep quality using the validated Arabic version of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index, anxiety disorders by the generalized anxiety disorder (GAD-7) scale, demographic characteristics, and clinical history.
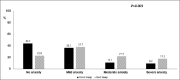
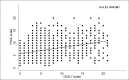
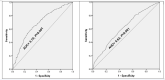
Results: Among the study participants (33.8% males, 46.2% healthcare workers, 25% had chronic diseases, 30.1% were physically active during lockdown, and 70.3% reported work termination due to COVID-19 infection, 68.4% complained of bad sleep and 70.3% showed clinically significant levels of anxiety). In multiple logistic regression analysis, bad sleep quality was significantly associated with moderate anxiety (OR: 1.88; [95% CI: 1.37-2.60]), severe anxiety (OR: 3.15; [95% CI: 2.18-4.55]), being physically active (OR: 0.53; [95% CI: 0.39-0.71]), received higher education as being postgraduate (OR: 0.56; [95% CI: 0.35-0.92]), or living with family (OR: 0.74; [95% CI :0.56-0.98]).The GAD-7 scale added 8% discrimination power for prediction of bad sleep quality compared to the model based on demographic and clinical data [with GAD: AUC=0.70, p<0.001; without GAD: AUC=0.62, p<0.001].
Conclusion: COVID-19 had a significant impact on sleep quality and anxiety among Egyptians. Since both the conditions may overlap and potentiate each other leading to chronic dysfunctional outcomes, an accurate assessment and clinical approach may favor a better prognosis.
Keywords: Anxiety; COVID-19; Egyptians; Sleep Quality.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): situation report - 51. Geneva: WHO; 2020.
-
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) COVID-19 pandemic humanity needs leadership and solidarity to defeat COVID-19 Egypt [Internet] Cairo: UNDP; 2020. Available from: https://www.eg.undp.org/content/egypt/en/home/coronavirus.html .
-
- Ministry of Health and Population (EGY) Egypt implements strong measures to fight COVID-19 [Internet] Cairo: Egyptian Government/Ministry of Health and Population; 2020. Available from: https://www.care.gov.eg/EgyptCare/Index.aspx .
-
- Altena E, Baglioni C, Espie CA, Ellis J, Gavriloff D, Holzinger B, et al. Dealing with sleep problems during home confinement due to the COVID-19 outbreak: Practical recommendations from a task force of the European CBT-I Academy. J Sleep Res. 2020 Aug;29(4):e13052. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
