Survival characteristics of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database study
- PMID: 35662983
- PMCID: PMC9153071
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i5.352
Survival characteristics of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database study
Abstract
Background: Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FL-HCC) is a rare and distinct type of hepatocellular carcinoma that frequently presents in an advanced stage in younger patients with no underlying liver disease. Currently, there is a limited understanding of factors that impact outcomes in FL-HCC.
Aim: To characterize the survival of FL-HCC by age, race, and surgical intervention.
Methods: This is a retrospective study of The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. We identified patients with FL-HCC between 2000-2018 by using an ICD-O-3 site code C22.0 and a histology code 8171/3: Hepatocellular carcinoma, fibrolamellar. In addition, demographics, tumor characteristics, types of surgical procedure, stages, and survival data were obtained. We conducted three separate survival analyses by age groups; ≤ 19, 20-59, and ≥ 60-year-old, and race; White, Black, Hispanic, Asian and Pacific islanders (API), and surgical types; Wedge resection or segmental resection, lobectomy, extended lobectomy (lobectomy + locoregional therapy or resection of the other lobe), and transplant. The Chi-Square test analyzed categorical variables, and continuous variables were examined using the Mann-Whitney U test. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve was used to compare survival. Multivariate analysis was done with Cox regression analysis.
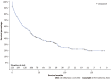
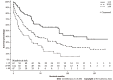
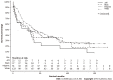
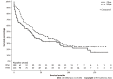
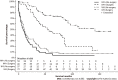
Results: We identified 225 FL-HCC patients with a mean age of 36.9. Overall median survival was 34 (95%CI: 27-41) mo. Patients ≤ 19-years-old had more advanced disease with positive lymph nodes status. However, they received more surgical interventions such as a wedge, segmental resection, lobectomy, extended lobectomy, and transplant. Survival for ≤ 19 was 85 (95%CI: 37-137) mo, age 20-59 was 29 (95%CI: 18-41) mo, and age ≥ 60 years was 12 (95%CI: 7-31) mo (P < 0.001). There were no differences in stage, lymph node status, metastasis status, and surgical treatment among races. The median survival were; Whites had 39 (95%CI: 29-63), Blacks 26 (95%CI: 5-92), Hispanics 31 (95%CI: 11-54), and APIs 28 (95%CI: 5-39) mo (P = 0.28). Of 225 patients, 111 FL-HCC patients had surgical procedures. Median survivals for a wedge or segmental resection was 112 (95%CI: 78-NA), lobectomy was 92 (95%CI: 57-NA), extended lobectomy was 54 (95%CI: 23-NA), and a transplant was 63 (95%CI: 20-NA) mo (P < 0.001). The median survival was better in patients who had surgical treatments regardless of lymph nodes or metastasis status (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: FL-HCC occurs in a primarily younger population, but survival can be prolonged despite the aggressive disease. There were no racial differences in the survival of FL-HCC; however, Asians with FL-HCC tended to be older than in other races. Surgical treatment provided better survival even in those patients with nodal disease or metastases. Although future studies are needed to explore other therapies for FL-HCC, surgical options should be considered in all cases of FL-HCC unless contraindicated.
Keywords: Age; Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma; Race; Survival; Transplant.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Wong LL is a speaker bureau for Eisai. All other authors do not have any conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Malouf GG, Job S, Paradis V, Fabre M, Brugières L, Saintigny P, Vescovo L, Belghiti J, Branchereau S, Faivre S, de Reyniès A, Raymond E. Transcriptional profiling of pure fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma reveals an endocrine signature. Hepatology . 2014;59:2228–2237. - PubMed
-
- Mavros MN, Mayo SC, Hyder O, Pawlik TM. A systematic review: treatment and prognosis of patients with fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg . 2012;215:820–830. - PubMed
-
- Paradis V. Histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent Results Cancer Res . 2013;190:21–32. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Chan KW, Wang B, Qiao L. Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol . 2009;104:2617–24; quiz 2625. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

