Advances in pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From genetics to lipidomics
- PMID: 35663007
- PMCID: PMC9134151
- DOI: 10.5409/wjcp.v11.i3.221
Advances in pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From genetics to lipidomics
Abstract
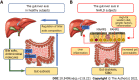
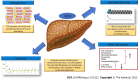
As a result of the obesity epidemic, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) represents a global medical concern in childhood with a closely related increased cardiometabolic risk. Knowledge on NAFLD pathophysiology has been largely expanded over the last decades. Besides the well-known key NAFLD genes (including the I148M variant of the PNPLA3 gene, the E167K allele of the TM6SF2, the GCKR gene, the MBOAT7-TMC4 rs641738 variant, and the rs72613567:TA variant in the HSD17B13 gene), an intriguing pathogenic role has also been demonstrated for the gut microbiota. More interestingly, evidence has added new factors involved in the "multiple hits" theory. In particular, omics determinants have been highlighted as potential innovative markers for NAFLD diagnosis and treatment. In fact, different branches of omics including metabolomics, lipidomics (in particular sphingolipids and ceramides), transcriptomics (including micro RNAs), epigenomics (such as DNA methylation), proteomics, and glycomics represent the most attractive pathogenic elements in NAFLD development, by providing insightful perspectives in this field. In this perspective, we aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of NAFLD pathophysiology in children, from the oldest pathogenic elements (including genetics) to the newest intriguing perspectives (such as omics branches).
Keywords: Fatty; Genetics; Lipidomics; Liver; Pediatric.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and kidney function: Effect of HSD17B13 variant.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Sep 28;26(36):5474-5483. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i36.5474. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33024398 Free PMC article.
-
Independent and joint correlation of PNPLA3 I148M and TM6SF2 E167K variants with the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Feb 24;19(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01207-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32093693 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effects of PNPLA3, TM6SF2 and HSD17B13 variants on severity of biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatol Int. 2021 Aug;15(4):922-933. doi: 10.1007/s12072-021-10200-y. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Hepatol Int. 2021. PMID: 34076851 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in paediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Role of lipidomics.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul 7;27(25):3815-3824. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i25.3815. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34321846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NAFLD and renal function in children: is there a genetic link?Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Sep;15(9):975-984. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1906649. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33851883 Review.
Cited by
-
[Risk analysis of serum chemical residues for metabolic associated fatty liver disease based on exposome-lipidome wide association study].Se Pu. 2024 Feb;42(2):164-175. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.12014. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38374597 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Sex Differences in Body Composition and MASLD in Children With Overweight and Obesity.Acta Paediatr. 2025 Jul;114(7):1709-1719. doi: 10.1111/apa.70026. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Acta Paediatr. 2025. PMID: 39945203 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the role of genetic variations in NAFLD: implications for disease pathogenesis and precision medicine approaches.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Mar 20;29(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01708-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38504356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variation and elevated liver enzymes during childhood, adolescence and early adulthood.Int J Epidemiol. 2023 Oct 5;52(5):1341-1349. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyad048. Int J Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 37105232 Free PMC article.
-
High-frequency variants in PKA signaling-related genes within a large pediatric cohort with obesity or metabolic abnormalities.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 13;14:1272939. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1272939. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38027204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldner D, Lavine JE. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Unique Considerations and Challenges. Gastroenterology . 2020;158:1967–1983.e1. - PubMed
-
- Shaunak M, Byrne CD, Davis N, Afolabi P, Faust SN, Davies JH. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and childhood obesity. Arch Dis Child . 2021;106:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Morandi A, Di Sessa A, Zusi C, Umano GR, El Mazloum D, Fornari E, Miraglia Del Giudice E, Targher G, Maffeis C. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Estimated Insulin Resistance in Obese Youth: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab . 2020;105 - PubMed
-
- Di Bonito P, Valerio G, Licenziati MR, Miraglia Del Giudice E, Baroni MG, Morandi A, Maffeis C, Campana G, Spreghini MR, Di Sessa A, Morino G, Crinò A, Chiesa C, Pacifico L, Manco M. High uric acid, reduced glomerular filtration rate and non-alcoholic fatty liver in young people with obesity. J Endocrinol Invest . 2020;43:461–468. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

