Performance evaluation of rhamnolipids addition for the biodegradation and bioutilization of petroleum pollutants during the composting of organic wastes with waste heavy oil
- PMID: 35663019
- PMCID: PMC9157225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104403
Performance evaluation of rhamnolipids addition for the biodegradation and bioutilization of petroleum pollutants during the composting of organic wastes with waste heavy oil
Abstract
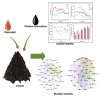
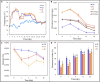
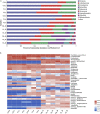
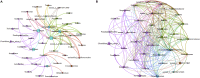
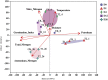
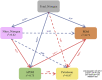
Environmental pollution caused by petroleum hydrocarbons is being paid more and more attention worldwide. Surfactants are able to improve the solubility of petroleum hydrocarbons, but their effects on petroleum hydrocarbon degradation in composting systems are still unclear. In this study, the effects on microbial community succession were investigated by adding petroleum hydrocarbons and rhamnolipids during composting of organic wastes. The results showed that the compost and the addition of rhamnolipids could effectively reduce the petroleum hydrocarbon content with an efficiency of 73.52%, compared to 53.81% for the treatment without addition. Network analyses and Structural Equation Model suggested that there were multiple potential petroleum degraders microbes that might be regulated by nitrogen. The findings in this study can also provide an implication for the treatment of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants from oil-polluted soil, and the technology can be potentially applied on an industrial scale in practice.
Keywords: Chemistry; Environmental chemistry; Surface chemistry.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bentonite addition enhances the biodegradation of petroleum pollutants and bacterial community succession during the aerobic co-composting of waste heavy oil with agricultural wastes.J Hazard Mater. 2024 Jan 15;462:132655. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132655. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Hazard Mater. 2024. PMID: 37827101
-
Biochar amendment of aerobic composting for the effective biodegradation of heavy oil and succession of bacterial community.Bioresour Technol. 2022 Oct;362:127820. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127820. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Bioresour Technol. 2022. PMID: 36028051
-
Total petroleum hydrocarbons and influencing factors in co-composting of rural sewage sludge and organic solid wastes.Environ Pollut. 2023 Feb 15;319:120911. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120911. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 36549453
-
Aerobic composting remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Current and future perspectives.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Jan 20;753:142250. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142250. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 33207468 Review.
-
Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons.Bioresour Technol. 2017 Jan;223:277-286. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.037. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Bioresour Technol. 2017. PMID: 27789112 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative analysis of the mouse fecal microbiome and metabolome reveal dynamic phenotypes in the development of colorectal cancer.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 28;13:1021325. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1021325. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36246263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abed R.M., Al-Sabahi J., Al-Maqrashi F., Al-Habsi A., Al-Hinai M. Characterization of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from oil-contaminated sediments in the Sultanate of Oman and evaluation of bioaugmentation and biostimulation approaches in microcosm experiments. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2014;89:58–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.01.006. - DOI
-
- Abed R.M.M., Al-Kharusi S., Al-Hinai M. Effect of biostimulation, temperature and salinity on respiration activities and bacterial community composition in an oil polluted desert soil. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2015;98:43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.11.018. - DOI
-
- Agency I.E., Schrder A. 2019. IEA World Energy Outlook 2019 - Section on Material Efficiency.
-
- Bao J., Wang X., Gu J., Dai X., Zhang K., Wang Q., Ma J., Peng H. Effects of macroporous adsorption resin on antibiotic resistance genes and the bacterial community during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020;295:121997. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

