Multimodal Imaging in Ocular Siderosis
- PMID: 35663927
- PMCID: PMC9164260
- DOI: 10.1177/2474126420962020
Multimodal Imaging in Ocular Siderosis
Abstract
Purpose: This report aims to characterize ocular changes in a case of ocular siderosis with iron toxicity using multimodal imaging and electroretinography.
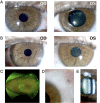
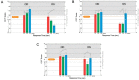
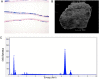
Methods: A 34-year-old woman presented with ocular siderosis of the left eye following penetrating injury with an iron-containing foreign body. The patient's uncorrected visual acuities were 20/60 and 20/150 in the right and left eye, respectively, with abnormal pupillary function and presence of a cataract in the left eye. She underwent successful intraocular foreign body removal and cataract surgery with no postoperative complications. Cone contrast threshold (CCT), full-field electroretinogram, spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT), and OCT angiography (OCTA) were used to characterize ocular alterations preoperatively and postoperatively.
Results: CCT color vision testing showed abnormal color vision, and OCTA revealed increased vascular flow density associated with the foreign body.
Conclusions: CCT color vision testing, OCTA, OCT, and full-field electroretinogram can characterize retinal changes in cases of ocular siderosis.
Keywords: OCT angiography; cular siderosis; full-field electroretinogram; intraocular foreign body; iron toxicity; optical coherence tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Xie H, Chen S. Ocular siderosis. Eye Sci. 2013;28(2):108–112. - PubMed
-
- Alldredge CD, Schlieve CR, Miller NR, Levin LA. Pathophysiology of the optic neuropathy associated with Friedreich ataxia. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121(11):1582–1585. doi:10.1001/archopht.121.11.1582 - PubMed
-
- Hope-Ross M, Mahon GJ, Johnston PB. Ocular siderosis. Eye (Lond). 1993;7(Pt 3):419–425. doi:10.1038/eye.1993.83 - PubMed

