Comparison of one anastomosis gastric bypass versus standard Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus a variant of biliopancreatic diversion, in a case-matched, non-superobese population: 6 years of follow-up
- PMID: 35664023
- PMCID: PMC9165332
- DOI: 10.5114/pg.2021.108453
Comparison of one anastomosis gastric bypass versus standard Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus a variant of biliopancreatic diversion, in a case-matched, non-superobese population: 6 years of follow-up
Abstract
Introduction: One anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB) is gaining increasing acceptance as a simple, safe, and effective operation for treating morbid obesity. Data comparing this procedure with the most effective biliopancreatic diversions (BPD) remain scarce, and most studies evaluate OAGB against standard Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB).
Aim: To present the mid-term results of a comparison of RYGB, OAGB, and our modification of BPD in an exclusively non-superobese population, regarding safety, efficacy, preservation of weight loss, as well as late postoperative metabolic and non-metabolic complications.
Material and methods: From our cohorts of patients treated for morbid obesity with OAGB, RYGB, and BPD at Patras University Hospital, we identified patients who had case-matched preoperative profiles regarding age, preoperative body mass index (BMI), and obesity-related comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidaemia). Thirty-four patients from each group were included in the study. Bariatric outcomes, non-metabolic complications, and postoperative metabolic parameters were followed until the 6th postoperative year.
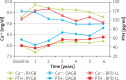
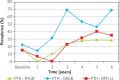
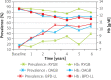
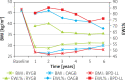
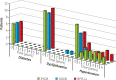
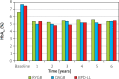
Results: The average patient age was 37.4 years (range: 19-57), 85.3% were female and 14.7% were male, with a mean BMI of 46.3 kg/m2 (range: 38.3-49.7). Regarding weight loss and glycaemic control, OAGB had comparable results to BPD and was significantly better than RYGB. The safety profile was analogous to RYGB, with the exception of calcium levels, which, even though they were within normal range, were significantly lower than those in RYGB. Comorbidities were successfully treated with all operations at comparable rates. In this cohort, no other major complications were observed.
Conclusions: OAGB offered mid-term results comparable to BPD while being safe and with minimal impact on the patient's nutritional state. It is an effective procedure for treating morbid obesity, which results in sustained weight loss and a high rate of resolution of comorbidities.
Keywords: biliopancreatic diversion; gastric bypass; metabolic deficiencies.
Copyright © 2022 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of one anastomosis gastric bypass versus Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for obesity (YOMEGA): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, non-inferiority trial.Lancet. 2019 Mar 30;393(10178):1299-1309. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30475-1. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 30851879 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass with One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass with a Biliopancreatic Limb of 200 or 160 cm: 1-Year Results of the Tehran Obesity Treatment Study (TOTS).Obes Surg. 2020 Sep;30(9):3528-3535. doi: 10.1007/s11695-020-04681-3. Obes Surg. 2020. PMID: 32405910
-
Long Biliopancreatic Limb Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass Versus One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass: a Randomized Controlled Study.Obes Surg. 2023 Jul;33(7):1966-1973. doi: 10.1007/s11695-023-06631-1. Epub 2023 May 13. Obes Surg. 2023. PMID: 37178225 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass Versus Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass for Obesity: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Obes Surg. 2020 Apr;30(4):1211-1218. doi: 10.1007/s11695-019-04288-3. Obes Surg. 2020. PMID: 31749109
-
Randomized Controlled Trial of One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass Versus Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass for Obesity: Comparison of the YOMEGA and Taiwan Studies.Obes Surg. 2019 Sep;29(9):3047-3053. doi: 10.1007/s11695-019-04065-2. Obes Surg. 2019. PMID: 31290104 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison between low molecular weight heparin and apixaban (direct oral anticoagulant) in the prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy.Obes Surg. 2025 Mar;35(3):934-940. doi: 10.1007/s11695-025-07721-y. Epub 2025 Feb 8. Obes Surg. 2025. PMID: 39921824 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Marginal Ulcers Following One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Obes Surg. 2023 Sep;33(9):2884-2897. doi: 10.1007/s11695-023-06762-5. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Obes Surg. 2023. PMID: 37526816
-
One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass as Revisional Surgery Following Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Obes Surg. 2024 Feb;34(2):429-441. doi: 10.1007/s11695-024-07056-0. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Obes Surg. 2024. PMID: 38198098
-
The impact of bariatric surgery procedures on the modulation of cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with severe obesity: a 12-month follow-up.J Int Med Res. 2022 Oct;50(10):3000605221119657. doi: 10.1177/03000605221119657. J Int Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36314880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maggard MA, Shugarman LR, Suttorp M, et al. . Metaanalysis: surgical treatment of obesity. Ann Intern Med 2005; 142: 547-59. - PubMed
-
- Buchwald H. Overview of bariatric surgery. J Am Coll Surg 2002; 194: 367-75. - PubMed
-
- Pournaras DJ, Aasheim ET, Bueter M, et al. . Effect of bypassing the proximal gut hormones involved with glycemic control and weight loss. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2012; 8: 371-4. - PubMed
-
- Chronaiou A, Tsoli M, Kehagias I, et al. . Lower ghrelin levels and exaggerated postprandial peptide-YY, glucagon-like peptide-1 and insulin responses, after gastric fundus resection, in patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a randomized clinical trial. Obes Surg 2012; 22: 1761-70. - PubMed
-
- Rutledge R, Walsh TR. Continued excellent results with the minigastric bypass: six-year study in 2,410 patients. Obes Surg 2005; 15: 1304-8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
