Discovery of Anilino-1,4-naphthoquinones as Potent EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Comprehensive Molecular Modeling
- PMID: 35664590
- PMCID: PMC9161259
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01188
Discovery of Anilino-1,4-naphthoquinones as Potent EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Comprehensive Molecular Modeling
Abstract
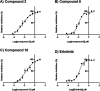
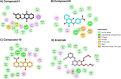
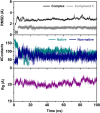
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has been recognized as one of the attractive targets for anticancer drug development. Herein, a set of anilino-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives (3-18) was synthesized and investigated for their anticancer and EGFR inhibitory potentials. Among all tested compounds, three derivatives (3, 8, and 10) were selected for studying EGFR inhibitory activity (in vitro and in silico) due to their most potent cytotoxic activities against six tested cancer cell lines (i.e., HuCCA-1, HepG2, A549, MOLT-3, MDA-MB-231, and T47D; IC50 values = 1.75-27.91 μM), high selectivity index (>20), and good predicted drug-like properties. The experimental results showed that these three promising compounds are potent EGFR inhibitors with nanomolar IC50 values (3.96-18.64 nM). Interestingly, the most potent compound 3 bearing 4-methyl substituent on the phenyl ring displayed 4-fold higher potency than the known EGFR inhibitor, erlotinib. Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, and MM/GBSA-based free energy calculation revealed that van der Waals force played a major role in the accommodations of compound 3 within the ATP-binding pocket of EGFR. Additionally, the 4-CH3 moiety of the compound was noted to be a key chemical feature contributing to the highly potent EGFR inhibitory activity via its formations of alkyl interactions with A743, K745, M766, and L788 residues as well as additional interactions with M766 and T790.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Discovery of Novel Naphthoquinone-Chalcone Hybrids as Potent FGFR1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Modeling.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 30;8(36):32593-32605. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03176. eCollection 2023 Sep 12. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37720749 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, anti-tumor activity, and molecular modeling of quinazoline and pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives targeting epidermal growth factor receptor.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Aug 8;118:276-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.04.026. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27132165
-
Design, synthesis, anticancer activity and docking studies of novel quinazoline-based thiazole derivatives as EGFR kinase inhibitors.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 20;9(9):e20300. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20300. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809937 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 2-(5-Aryl-4,5-Dihydropyrazol-1-yl)thiazol-4-One as EGFR Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Assessment and Molecular Docking Insights.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 May 16;16:1457-1471. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S356988. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35607598 Free PMC article.
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
Cited by
-
Anilino-1,4-naphthoquinones as potent mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: in vitro and in silico studies.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024 Dec;39(1):2357174. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2357174. Epub 2024 May 30. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38814149 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Potential of Aminonaphthoquinone Derivatives Against Amyloid Beta-Induced Neuronal Cell Death Through Modulation of SIRT1 and BACE1.Neurochem Res. 2024 Dec 7;50(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04281-y. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 39644364 Free PMC article.
-
Quinoxalinones as A Novel Inhibitor Scaffold for EGFR (L858R/T790M/C797S) Tyrosine Kinase: Molecular Docking, Biological Evaluations, and Computational Insights.Molecules. 2022 Dec 14;27(24):8901. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248901. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558033 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal potential, mechanism of action, and toxicity of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives.Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2024 Aug 23;14(3):289-295. doi: 10.1556/1886.2024.00072. Print 2024 Sep 11. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2024. PMID: 39178045 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel Naphthoquinone-Chalcone Hybrids as Potent FGFR1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Modeling.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 30;8(36):32593-32605. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03176. eCollection 2023 Sep 12. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37720749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang C.-H.; Chou H.-C.; Fu Y.-N.; Yeh C.-L.; Cheng H.-W.; Chang I.-C.; Liu K.-J.; Chang G.-C.; Tsai T.-F.; Tsai S.-F.; Liu H.-P.; Wu Y.-C.; Chen Y.-T.; Huang S.-F.; Chen Y.-R. EGFR over-expression in non-small cell lung cancers harboring EGFR mutations is associated with marked down-regulation of CD82. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1540–1549. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.04.020. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

