Association of MicroRNAs With Risk of Stroke: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35665049
- PMCID: PMC9160310
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.865265
Association of MicroRNAs With Risk of Stroke: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Altered expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) may contribute to disease vulnerability. Studies have reported the involvement of miRNA in the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke.
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis of data from 6 studies that used a panel of miRNAs with altered expressions to diagnose ischemic stroke with the Bayesian framework. The I 2 test and Cochran's Q-statistic were used to assess heterogeneity. Funnel plots were generated and publication bias was assessed using Begg and Egger tests.
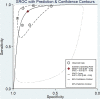
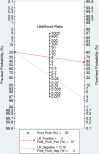
Results: On summary receiver operating characteristics (SROC) curve analysis, the pooled sensitivity and specificity of altered miRNA expressions for diagnosis of ischemic stroke was 0.92 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.80-0.97) and 0.83 (95% CI 0.71-0.90), respectively; the diagnostic odds ratio was 54.35 (95% CI 20.39-144.92), and the area under the SROC curve was 0.93 (95% CI 0.90-0.95).
Conclusions: Our results showed a link between dysregulation of miRNAs and the occurrence of ischemic stroke. Abnormal miRNA expression may be a potential biomarker for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: diagnostic odds ratio; ischemic stroke; meta-analysis; microRNA; sensitivity.
Copyright © 2022 Deng, Huang, Zhang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

