Maintenance Outcomes of the Children's Healthy Living Program on Overweight, Obesity, and Acanthosis Nigricans Among Young Children in the US-Affiliated Pacific Region: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35666503
- PMCID: PMC9171559
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.14802
Maintenance Outcomes of the Children's Healthy Living Program on Overweight, Obesity, and Acanthosis Nigricans Among Young Children in the US-Affiliated Pacific Region: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Few obesity prevention trials among children have demonstrated sustainable outcomes in the long term.
Objectives: To sustain a community-wide decrease in the prevalence of overweight and obesity among young children in the US-affiliated Pacific region.
Design, setting, and participants: In the Children's Healthy Living community-randomized clinical trial, hierarchical modeling comparing the change in intervention and control communities accounted for community randomization (community clustering with jurisdictions), and adjusted for the age and sex distribution of the assessed children in a cross-sectional design. The outcome measures were repeated in communities rather than among individual children. A total of 27 communities in 5 jurisdictions (Hawai'i, Alaska, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, American Samoa, and Guam) of the US-affiliated Pacific region were included. Participants included children aged 2 to 8 years in the 27 selected communities from October 1, 2012 (4329 in time 1 [baseline]) to August 31, 2015 (4043 in time 2 [intervention end]) and from January 1, 2019, to April 30, 2020 (1469 in time 3 [maintenance period]). Study analysis was completed March 25, 2022.
Interventions: Nineteen activities addressed training, policies, systems, and environments of communities and 6 target behaviors of children (consumption of fruit and vegetables, water, and sugar-sweetened beverages; sleep; physical activity; and screen time) during a 2-year intervention period. Continued partnership with community coalitions, ongoing academic training of community partners, and use of trial data during a 6-year maintenance period.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was measured anthropometry; secondary outcomes were the presence of acanthosis nigricans, dietary intake derived from 2 days of food records, and survey questions on screen time and sleep disturbance.
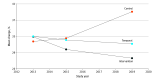
Results: Among the 9840 children included in the analysis (4866 girls [49.5%] and 4974 boys [50.5%]; 6334 [64.4%] aged 2-5 years), the intervention group showed significant improvements compared with the control group from times 1 to 3 in prevalence of overweight plus obesity (d = -12.60% [95% CI, -20.92% to -4.28%]), waist circumference (d = -1.64 [95% CI, -2.87 to -0.41] cm), and acanthosis nigricans prevalence (d = -3.55% [95% CI, -6.17% to -0.92%]). Significant improvements were also observed from times 2 to 3 in prevalence of overweight plus obesity (d = -8.73% [95% CI, -15.86% to -1.60%]) but not in waist circumference (d = -0.81 [95% CI, -1.85 to 0.23] cm).
Conclusions and relevance: This randomized clinical trial found that the outcomes of the Children's Healthy Living intervention were maintained and enhanced 6 years after the intervention among young children in the US-affiliated Pacific region. The prevalence of overweight, obesity, and acanthosis nigricans was further reduced in communities, suggesting that multilevel multicomponent interventions may help reduce child overweight and obesity in this region.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01881373.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Novotny R, Fialkowski MK, Li F, et al. Systematic review of prevalence of young child overweight and obesity in the United States–affiliated Pacific region compared with the 48 contiguous states: the Children’s Healthy Living Program. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(1):e22-e35. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2014.302283 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Novotny R, Li F, Fialkowski MK, et al. ; Children’s Healthy Living (CHL) Program . Prevalence of obesity and acanthosis nigricans among young children in the Children’s Healthy Living Program in the United States Affiliated Pacific. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(37):e4711. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004711 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous