Leptomeningeal metastases in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer: Real-world data from a multicentric European cohort
- PMID: 35666525
- PMCID: PMC9540903
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.34135
Leptomeningeal metastases in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer: Real-world data from a multicentric European cohort
Abstract
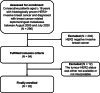
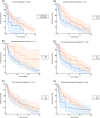
In patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive (HER2+) breast cancer, leptomeningeal metastases (LM) are a rare but often a fatal clinical scenario. In this multicentric study, clinical and pathologic characteristics of patients with HER2+ breast cancer developing LM were described, as well as survival outcomes. Data were gathered retrospectively from medical records of 82 patients with advanced HER2+ breast cancer and LM treated between August 2005 and July 2020. Following LM diagnosis, 79 (96.3%) patients received at least one line of anti-HER2 therapy, 25 (30.5%) patients received intrathecal therapy and 58 (70.7%) patients received radiotherapy. Overall survival (OS) was 8.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 5.7-11), 1-year OS was 42%, and 2-year OS was 21%. At univariate analysis, patients who were treated after 2010, had better Karnofsky performance status, were free of neurological symptoms, had better prognostic, received chemotherapy (OS difference 9.4 months, P = .024), or monoclonal antibodies (trastuzumab ± pertuzumab; OS difference 6.1 months; P = .013) after LM diagnosis, had a statistically significantly longer OS. Presence of neurological symptoms (hazard ratio 3.32, 95% CI 1.26-8.73; P = .015) and not having received radiotherapy (hazard ratio 2.02, 95% CI 1.09-3.72; P = .024) were all associated with poorer OS at multivariate analysis. To summarize, not having neurological symptoms and receiving RT at LM diagnosis were associated with prolonged OS in our cohort. Survival seemed to be prolonged with multimodality treatment, which included targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and RT to the LM sites.
Keywords: anti-HER2 therapy; breast cancer; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; leptomeningeal metastases; radiation therapy.
© 2022 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Ivica Ratosa, Nika Dobnikar, Michele Bottosso, Amélie Darlix, William Jacot, Stéphane Pouderoux, Domen Ribnikar, Léa Sinoquet and Tanja Znidaric report no conflict of interest. Maria Vittoria Dieci reports personal fees from Eli Lilly, MSD, Exact Sciences, Novartis, Pfizer, Seagen, outside the submitted work. Valentina Guarneri reports personal fees from Eli Lilly, Novartis, Roche, MSD, Gilead, Eisai (Advisory Board), and from Eli Lilly, Novartis, GSK, Amgen (Speakers' Bureau) outside the submitted work. Gaia Griguolo reports personal fees from Eli Lilly and Novartis (invited speaker), Gilead (Advisory Board) and from Novartis, Pfizer, Amgen, Daiichi Sankyo (Travel Support) outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrathecal trastuzumab versus alternate routes of delivery for HER2-targeted therapies in patients with HER2+ breast cancer leptomeningeal metastases.Breast. 2023 Jun;69:451-468. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2023.04.008. Epub 2023 May 1. Breast. 2023. PMID: 37156650 Free PMC article.
-
Survival benefit of anti-HER2 therapy after whole-brain radiotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer patients with brain metastasis.Breast Cancer. 2016 Sep;23(5):732-9. doi: 10.1007/s12282-015-0631-x. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Breast Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26267412 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of intrathecal administration of trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer with leptomeningeal metastasis.Neuro Oncol. 2023 Feb 14;25(2):365-374. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noac180. Neuro Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35868630 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
T-DM1 Efficacy in Patients With HER2-positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Progressing After a Taxane Plus Pertuzumab and Trastuzumab: An Italian Multicenter Observational Study.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Apr;20(2):e181-e187. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31735691
-
Trastuzumab combined with doublet or single-agent chemotherapy as first-line therapy for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Apr;168(2):337-348. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4592-y. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29188398 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Complete Cerebrospinal Fluid Response to T-DM1 in HER2 Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Case Report.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 10;13(3):756. doi: 10.3390/life13030756. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983911 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical considerations of CDK4/6 inhibitors in HER2 positive breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 16;13:1322078. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1322078. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38293701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with metastatic breast cancer and leptomeningeal disease: a single center retrospective cohort study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Aug;206(3):625-636. doi: 10.1007/s10549-024-07339-1. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38888796 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal trastuzumab versus alternate routes of delivery for HER2-targeted therapies in patients with HER2+ breast cancer leptomeningeal metastases.Breast. 2023 Jun;69:451-468. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2023.04.008. Epub 2023 May 1. Breast. 2023. PMID: 37156650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bendell JC, Domchek SM, Burstein HJ, et al. Central nervous system metastases in women who receive trastuzumab‐based therapy for metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;97(12):2972‐2977. - PubMed
-
- Lee YT. Breast carcinoma: pattern of metastasis at autopsy. J Surg Oncol. 1983;23(3):175‐180. - PubMed
-
- Lamovec J, Zidar A. Association of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in carcinoma of the breast with infiltrating lobular carcinoma. An autopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1991;115:507‐510. - PubMed
-
- Palmieri D, Bronder JL, Herring JM, et al. Her‐2 overexpression increases the metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer cells in the brain. Cancer Res. 2007;67(9):4190‐4198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

