WASP family proteins: Molecular mechanisms and implications in human disease
- PMID: 35667337
- PMCID: PMC9357188
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2022.151244
WASP family proteins: Molecular mechanisms and implications in human disease
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "WASP Family Proteins: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease" [Eur. J. Cell Biol. Vol. 101, Issue 3, (2022) 151244].Eur J Cell Biol. 2023 Mar;102(1):151287. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2023.151287. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Eur J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36635185 No abstract available.
Abstract
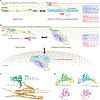
Proteins of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family play a central role in regulating actin cytoskeletal dynamics in a wide range of cellular processes. Genetic mutations or misregulation of these proteins are tightly associated with many diseases. The WASP-family proteins act by transmitting various upstream signals to their conserved WH2-Central-Acidic (WCA) peptide sequence at the C-terminus, which in turn binds to the Arp2/3 complex to stimulate the formation of branched actin networks at membranes. Despite this common feature, the regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of distinct WASP-family proteins are very different. Here, we summarize and clarify our current understanding of WASP-family proteins and how disruption of their functions is related to human disease.
Keywords: Actin; Arp2/3; Cyfip; HEM; JMY; SCAR; SHRC; SWIP; Sra1; Strumpellin; VCA; WASH; WASP; WAVE; WCA; WHAMM; WHIMP; WRC; Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Figures
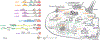
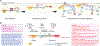


References
-
- Alkhairy OK, Rezaei N, Graham RR, Abolhassani H, Borte S, Hultenby K, Wu C, Aghamohammadi A, Williams DA, Behrens TW, Hammarström L, Pan-Hammarström Q, 2015. RAC2 loss-of-function mutation in 2 siblings with characteristics of common variable immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 135, 1380–1384.e5. 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.10.039 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

