The humoral response of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in hematological diseases: The HEMVACO study
- PMID: 35667558
- PMCID: PMC9164434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idnow.2022.05.008
The humoral response of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in hematological diseases: The HEMVACO study
Abstract
Objectives: The HEMVACO study evaluated the humoral response after mRNA anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in an hematological cohort.
Methods: HEMVACO was a prospective, multicentric study registered in ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT04852796. Patients received two or three doses of BNT162b2 vaccine or mRNA-1273 vaccine. The SARS-CoV-2 TrimericS IgG titers were measured 1, 3, 6 and 12 months after the second dose.
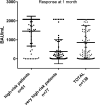
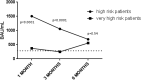
Results: Only 16 patients (11.6%) were naive of hematological treatment and 77 patients (55.8%) were on active treatment for hemopathy. Among the 138 analyzed patients, positive antibody titer at 1 month was obtained in 68.1% of patients with mean serology at 850±883 BAU/ml. Risk factors for vaccine failure were anti-CD20 therapy (OR=111[14.3-873]; P<0.001), hypogammaglobulinemia under 8g/L (OR=2.49[1.05-5.92]; P=0.032) and lymphopenia under 1.5G/L (OR=2.47[1.18-5.17]; P=0.015). Anti-CD20 therapy induced no anti-SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion (96%). Seventy-eight patients (56.5%) received a third dose and could reach the SARS-CoV-2 TrimericS IgG titer of high-risk patients (P=0.54). The median titer at 379 BAU/ml distinguished two groups of vaccine response (99±121 BAU/ml versus 1,109±678 BAU/ml).
Conclusion: Vaccination should be performed before anti-CD20 therapy if the hemopathy treatment can be delayed. Administration of the third vaccine dose was interesting for patients with suboptimal response, defined by a 379 BAU/ml titer in our study.
Keywords: Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody; Booster immunization; Hematologic diseases; Hypogammaglobulinemia; SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- van der Kolk L.E., Baars J.W., Prins M.H., van Oers M.H.J. Rituximab treatment results in impaired secondary humoral immune responsiveness. Blood. 2002;100(6):2257–2259. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

