Primary breast diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 35667697
- PMCID: PMC9171281
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-250478
Primary breast diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract
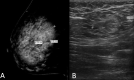
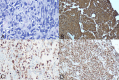
Primary breast lymphoma (PBL) is an uncommon type of breast malignancy. Its clinical presentation and radiographic findings are non-specific and overlap with breast carcinoma. The treatment of PBL differs significantly from breast carcinomas. Here we present a middle-aged woman who presented with an enlarging palpable right breast mass. Mammogram showed breast imaging-reporting and data system 4 findings. Breast mass biopsy pathology confirmed diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Although uncommon, clinicians should be cognisant of the possibility of PBL when patients present with a breast mass. Accurate diagnosis is essential to avoid unnecessary mastectomies.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Breast surgery; Malignant and Benign haematology; Medical management.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
