Cost-effectiveness of DPYD Genotyping Prior to Fluoropyrimidine-based Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer
- PMID: 35668003
- PMCID: PMC10496767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clcc.2022.05.001
Cost-effectiveness of DPYD Genotyping Prior to Fluoropyrimidine-based Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer
Abstract
Background: Adjuvant fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy substantially reduces recurrence and mortality after resection of stage 3 colon cancer. While standard doses of 5-fluorouracil and capecitabine are safe for most patients, the risk of severe toxicity is increased for the approximately 6% of patients with dihydropyimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) deficiency caused by pathogenic DPYD gene variants. Pre-treatment screening for pathogenic DPYD gene variants reduces severe toxicity but has not been widely adopted in the United States.
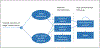
Methods: We conducted a cost-effectiveness analysis of DPYD genotyping prior to fluoropyrimidine-based adjuvant chemotherapy for stage 3 colon cancer, covering the c.1129-5923C>G (HapB3), c.1679T>G (*13), c.1905+1G>A (*2A), and c.2846A>T gene variants. We used a Markov model with a 5-year horizon, taking a United States healthcare perspective. Simulated patients with pathogenic DPYD gene variants received reduced-dose fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy. The primary outcome was the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) for DPYD genotyping.
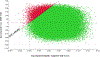
Results: Compared with no screening for DPD deficiency, DPYD genotyping increased per-patient costs by $78 and improved survival by 0.0038 quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), leading to an ICER of $20,506/QALY. In 1-way sensitivity analyses, The ICER exceeded $50,000 per QALY when the cost of the DPYD genotyping assay was greater than $286. In probabilistic sensitivity analysis using a willingness-to-pay threshold of $50,000/QALY DPYD genotyping was preferred to no screening in 96.2% of iterations.
Conclusion: Among patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for stage 3 colon cancer, screening for DPD deficiency with DPYD genotyping is a cost-effective strategy for preventing infrequent but severe and sometimes fatal toxicities of fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; Capecitabine; DPD deficiency; Pharmacogenetics.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement The authors attest that they have no financial conflicts of interest related to the topic of this research manuscript. Dr. Brooks reports consulting payments (unrelated to the topic of this manuscript) from CareCentrix, UnitedHealthcare, and Ipsen.
Figures
References
-
- Meyers BM, Cosby R, Quereshy F, Jonker D. Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Stage II and III Colon Cancer Following Complete Resection: A Cancer Care Ontario Systematic Review. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2017;29:459–465. - PubMed
-
- Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2343–2351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

