Combining SNP-to-gene linking strategies to identify disease genes and assess disease omnigenicity
- PMID: 35668300
- PMCID: PMC9894581
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01087-y
Combining SNP-to-gene linking strategies to identify disease genes and assess disease omnigenicity
Abstract
Disease-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) generally do not implicate target genes, as most disease SNPs are regulatory. Many SNP-to-gene (S2G) linking strategies have been developed to link regulatory SNPs to the genes that they regulate in cis. Here, we developed a heritability-based framework for evaluating and combining different S2G strategies to optimize their informativeness for common disease risk. Our optimal combined S2G strategy (cS2G) included seven constituent S2G strategies and achieved a precision of 0.75 and a recall of 0.33, more than doubling the recall of any individual strategy. We applied cS2G to fine-mapping results for 49 UK Biobank diseases/traits to predict 5,095 causal SNP-gene-disease triplets (with S2G-derived functional interpretation) with high confidence. We further applied cS2G to provide an empirical assessment of disease omnigenicity; we determined that the top 1% of genes explained roughly half of the SNP heritability linked to all genes and that gene-level architectures vary with variant allele frequency.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
C.P.F. is now an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

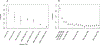


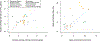






Comment in
-
One step closer to linking GWAS SNPs with the right genes.Nat Genet. 2022 Jun;54(6):748-749. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01093-0. Nat Genet. 2022. PMID: 35668299 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R37 MH107649/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HG010160/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HG012009/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH115676/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG012203/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109978/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH101244/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States

