Diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma release assays for diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35668411
- PMCID: PMC9169405
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-022-02013-y
Diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma release assays for diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis (SNPTB) is challenging. Interferon gamma-release assays (IGRAs) may be helpful in early diagnosis among these patients resulting in prompt treatment and favorable outcomes.
Methods: We performed a comprehensive search from each databases' inception to April 5, 2021. The studies that provided sufficient data regarding the sensitivity and specificity of IGRAs included QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube (QFT-GIT), T-SPOT.TB, or QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus for diagnosis of SNPTB were included.
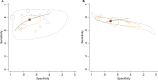
Results: Of 1,312 studies screened, 16 studies were included; 11 QFT-GIT, 2 T-SPOT.TB, and 3 QFT-GIT and T-SPOT.TB. For diagnosis of SNPTB, QFT-GIT had sensitivity of 0.77 (95% CI 0.71-0.82), specificity of 0.70 (95% CI 0.58-0.80), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 8.03 (95% CI 4.51-14.31), positive likelihood ratio (LR) of 2.61 (95% CI 1.80-3.80), negative LR of 0.33 (95% CI 0.25-0.42), and area under receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) of 0.81 (95% CI 0.77-0.84). T-SPOT.TB had sensitivity of 0.74 (95% CI 0.71-0.78), specificity of 0.71 (95% CI 0.49-0.86), DOR of 6.96 (95% CI 2.31-20.98), positive LR of 2.53 (95% CI 1.26-5.07), negative LR of 0.36 (95% CI 0.24-0.55), and AUROC of 0.77 (95% CI 0.73-0.80). The specificity seemed lower in the subgroup analyses of studies from high tuberculosis burden counties compared to the studies from low tuberculosis burden.
Conclusion: IGRAs do have insufficient diagnostic performance for SNPTB. However, the tests are still helpful to exclude tuberculosis among patients with low pre-test probability. Registry: PROSPERO: CRD42021274653.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Interferon-gamma release assays; Meta-analysis; Sensitivity; Smear-negative; Specificity; Tuberculosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interferon gamma release assays for Diagnostic Evaluation of Active tuberculosis (IDEA): test accuracy study and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2019 May;23(23):1-152. doi: 10.3310/hta23230. Health Technol Assess. 2019. PMID: 31138395 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity and specificity of QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus compared with QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube and T-SPOT.TB on active tuberculosis in Japan.J Infect Chemother. 2018 Mar;24(3):188-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Nov 3. J Infect Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29108749
-
Comparison of the QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube interferon-γ release assays: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Adv Med Sci. 2019 Sep;64(2):437-443. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Adv Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31586819
-
Can Interferon-γ Release Assays Be Useful for Monitoring the Response to Anti-tuberculosis Treatment?: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2020 Feb 3;68(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s00005-020-00568-4. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2020. PMID: 32016610
-
[Comparison of QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In Tube in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2022 May 12;45(5):445-452. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20220206-00095. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35527459 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Retrospective analysis of the clinical utility of multi-cytokine profiles in smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis.Saudi Med J. 2024 Jul;45(7):658-666. doi: 10.15537/smj.2024.45.7.20240310. Saudi Med J. 2024. PMID: 38955446 Free PMC article.
-
Portable paper-based electrochemiluminescence test incorporating lateral-flow immunosensors for detection of interferon-γ levels.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 7;11:1131840. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1131840. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36824352 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy study of STANDARD TB-Feron FIA and STANDARD TB-Feron ELISA tests for tuberculosis infection diagnosis in Eastern European setting.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2025 Mar 14;39:100518. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2025.100518. eCollection 2025 May. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2025. PMID: 40177661 Free PMC article.
-
How to diagnose TB in migrants? A systematic review of reviews and decision tree analytical modelling exercise to evaluate properties for single and combined tuberculosis screening tests.Eur Respir J. 2025 Jul 24;66(1):2402000. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02000-2024. Print 2025 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40268506 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Nanopore Sequencing for Diagnosing Pulmonary Tuberculosis Using Negative Smear Clinical Specimens.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Feb 19;17:673-682. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S442229. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38405053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global tuberculosis report 2021. https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa....
-
- Cattamanchi A, Ssewenyana I, Davis JL, Huang L, Worodria W, den Boon S, Yoo S, Andama A, Hopewell PC, Cao H. Role of interferon-gamma release assays in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with advanced HIV infection. BMC Infect Dis. 2010;10:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-75. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

