Systems analysis and improvement approach to optimize outpatient mental health treatment cascades in Mozambique (SAIA-MH): study protocol for a cluster randomized trial
- PMID: 35668423
- PMCID: PMC9169330
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-022-01213-8
Systems analysis and improvement approach to optimize outpatient mental health treatment cascades in Mozambique (SAIA-MH): study protocol for a cluster randomized trial
Abstract
Background: Significant investments are being made to close the mental health (MH) treatment gap, which often exceeds 90% in many low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). However, limited attention has been paid to patient quality of care in nascent and evolving LMIC MH systems. In system assessments across sub-Saharan Africa, MH loss-to-follow-up often exceeds 50% and sub-optimal medication adherence often exceeds 60%. This study aims to fill a gap of evidence-based implementation strategies targeting the optimization of MH treatment cascades in LMICs by testing a low-cost multicomponent implementation strategy integrated into routine government MH care in Mozambique.
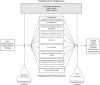
Methods: Using a cluster-randomized trial design, 16 clinics (8 intervention and 8 control) providing primary MH care will be randomized to the Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach for Mental Health (SAIA-MH) or an attentional placebo control. SAIA-MH is a multicomponent implementation strategy blending external facilitation, clinical consultation, and provider team meetings with system-engineering tools in an overall continuous quality improvement framework. Following a 6-month baseline period, intervention facilities will implement the SAIA-MH strategy for a 2-year intensive implementation period, followed by a 1-year sustainment phase. Primary outcomes will be the proportion of all patients diagnosed with a MH condition and receiving pharmaceutical-based treatment who achieve functional improvement, adherence to medication, and retention in MH care. The Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) will be used to assess determinants of implementation success. Specific Aim 1b will include the evaluation of mechanisms of the SAIA-MH strategy using longitudinal structural equation modeling as well as specific aim 2 estimating cost and cost-effectiveness of scaling-up SAIA-MH in Mozambique to provincial and national levels.
Discussion: This study is innovative in being the first, to our knowledge, to test a multicomponent implementation strategy for MH care cascade optimization in LMICs. By design, SAIA-MH is a low-cost strategy to generate contextually relevant solutions to barriers to effective primary MH care, and thus focuses on system improvements that can be sustained over the long term. Since SAIA-MH is integrated into routine government MH service delivery, this pragmatic trial has the potential to inform potential SAIA-MH scale-up in Mozambique and other similar LMICs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov; NCT05103033 ; 11/2/2021.
Keywords: Cluster randomized trial; Continuous quality improvement; Global mental health; Mozambique; Optimization of care cascades; Primary mental healthcare; Process mapping; Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach (SAIA); Systems engineering; Task-sharing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optimizing treatment cascades for mental healthcare in Mozambique: preliminary effectiveness of the Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach for Mental Health (SAIA-MH).Health Policy Plan. 2021 Feb 16;35(10):1354-1363. doi: 10.1093/heapol/czaa114. Health Policy Plan. 2021. PMID: 33221835 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling-up the Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach for prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in Mozambique (SAIA-SCALE): a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial.Implement Sci. 2019 Apr 27;14(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13012-019-0889-z. Implement Sci. 2019. PMID: 31029171 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systems analysis and improvement approach to optimize the hypertension diagnosis and care cascade for PLHIV individuals (SAIA-HTN): a hybrid type III cluster randomized trial.Implement Sci. 2020 Mar 6;15(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13012-020-0973-4. Implement Sci. 2020. PMID: 32143657 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Integrated care for mental health in epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-synthesis by the International League Against Epilepsy Integrated Mental Health Care Pathways Task Force.Epilepsia. 2025 Apr;66(4):1024-1040. doi: 10.1111/epi.18252. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Epilepsia. 2025. PMID: 39868988 Free PMC article.
-
Successful ingredients of effective Collaborative Care programs in low- and middle-income countries: A rapid review.Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2023 Mar 17;10:e11. doi: 10.1017/gmh.2022.60. eCollection 2023. Glob Ment Health (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37854388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mental health care cascade performance and associated factors: longitudinal analyses of routine Ministry of Health services in Mozambique.BMJ Public Health. 2025 Mar 13;3(1):e001024. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2024-001024. eCollection 2025. BMJ Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40099137 Free PMC article.
-
The Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach: specifying core components of an implementation strategy to optimize care cascades in public health.Implement Sci Commun. 2023 Feb 14;4(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s43058-023-00390-x. Implement Sci Commun. 2023. PMID: 36788577 Free PMC article.
-
Water, food, and mental well-being: Associations between drinking water source, household water and food insecurity, and mental well-being of low-income pregnant women in urban Mozambique.PLOS Water. 2024 Jun 20;3(6):e0000219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pwat.0000219. PLOS Water. 2024. PMID: 39949388 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing drivers of implementing "Scaling-up the Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach" for Prevention of Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission in Mozambique (SAIA-SCALE) over implementation waves.Implement Sci Commun. 2023 Jul 24;4(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s43058-023-00422-6. Implement Sci Commun. 2023. PMID: 37488632 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling-up and scaling-out the Systems Analysis and Improvement Approach to optimize the hypertension diagnosis and care cascade for HIV infected individuals (SCALE SAIA-HTN): a stepped-wedge cluster randomized trial.Implement Sci Commun. 2024 Mar 20;5(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s43058-024-00564-1. Implement Sci Commun. 2024. PMID: 38509605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) GBD Compare Data Visualization: Mozambique. 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

