Survival benefits from afatinib compared with gefitinib and erlotinib among patients with common EGFR mutation in first-line setting
- PMID: 35668712
- PMCID: PMC9284183
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14528
Survival benefits from afatinib compared with gefitinib and erlotinib among patients with common EGFR mutation in first-line setting
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are recommended as first-line treatment in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with sensitizing EGFR mutations. The sequential use of different EGFR-TKIs has been reported to demonstrate improvement in overall survival of NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations. There are limited reports on comparisons between regimens with first-line use of afatinib, gefitinib or erlotinib, followed by osimertinib upon disease progression with acquired T790M mutation.
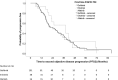
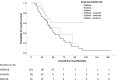
Methods: A retrospective cohort study of Chinese patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations who received first-line gefitinib, erlotinib or afatinib treatment, followed by osimertinib upon disease progression with acquired T790M mutation, was conducted. The differences in overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) with first-line EGFR-TKI (PFS1) and time to second objective disease progression (PFS2) were compared among patients on different first-line EGFR-TKIs.
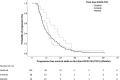
Results: Among 155 patients, 101 (65.2%), 38 (24.5%) and 16 (10.3%) patients were on first-line gefitinib, erlotinib or afatinib, respectively. Patients treated with afatinib in the first-line setting had significantly longer OS compared with those on gefitinib or erlotinib, while the PFS1 and PFS2 were longer for patients on afatinib but did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusions: First-line afatinib, followed by osimertinib upon disease progression with T790M mutation, demonstrated significantly longer OS compared to that using other EGFR-TKI in the first-line setting.
Keywords: T790M; afatinib; erlotinib; gefitinib; osimertinib.
© 2022 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, Novello S, Smit EF, Faivre‐Finn C, et al. Correction to: “metastatic non‐small cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up”. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(5):863–70. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first‐line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG‐0802): a multicentre, open‐label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2011;12(8):735–42. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, et al. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first‐line treatment of EGFR mutation‐positive advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG‐0802). Ann Oncol 2015;26(9):1877–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous