Tangled quest of post-COVID-19 infection-caused neuropathology and what 3P nano-bio-medicine can solve?
- PMID: 35668839
- PMCID: PMC9160520
- DOI: 10.1007/s13167-022-00285-2
Tangled quest of post-COVID-19 infection-caused neuropathology and what 3P nano-bio-medicine can solve?
Abstract
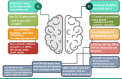
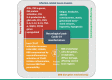
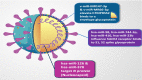
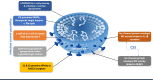
COVID-19-caused neurological problems are the important post-CoV-2 infection complications, which are recorded in ~ 40% of critically ill COVID-19 patients. Neurodegeneration (ND) is one of the most serious complications. It is necessary to understand its molecular mechanism(s), define research gaps to direct research to, hopefully, design new treatment modalities, for predictive diagnosis, patient stratification, targeted prevention, prognostic assessment, and personalized medical services for this type of complication. Individualized nano-bio-medicine combines nano-medicine (NM) with clinical and molecular biomarkers based on omics data to improve during- and post-illness management or post-infection prognosis, in addition to personalized dosage profiling and drug selection for maximum treatment efficacy, safety with least side-effects. This review will enumerate proteins, receptors, and enzymes involved in CoV-2 entrance into the central nervous system (CNS) via the blood-brain barrier (BBB), and list the repercussions after that entry, ranging from neuroinflammation to neurological symptoms disruption mechanism. Moreover, molecular mechanisms that mediate the host effect or viral detrimental effect on the host are discussed here, including autophagy, non-coding RNAs, inflammasome, and other molecular mechanisms of CoV-2 infection neuro-affection that are defined here as hallmarks of neuropathology related to COVID-19 infection. Thus, a couple of questions are raised; for example, "What are the hallmarks of neurodegeneration during COVID-19 infection?" and "Are epigenetics promising solution against post-COVID-19 neurodegeneration?" In addition, nano-formulas might be a better novel treatment for COVID-19 neurological complications, which raises one more question, "What are the challenges of nano-bio-based nanocarriers pre- or post-COVID-19 infection?" especially in the light of omics-based changes/challenges, research, and clinical practice in the framework of predictive preventive personalized medicine (PPPM / 3P medicine).
Keywords: 3P nano-bio-medicine; Autophagy; Biomarker; Blood–brain barrier (BBB); Central nervous system (CNS); Hallmarks of neuropathology; Inflammasome; Multi-omics; Nano-medicine (NM); Nanotechnology; Neurodegeneration; Non-coding RNAs (ncRNA); Patient stratification; Personalized medical service; Post-COVID-19 complications; Post-CoV-2 infection; Predictive diagnosis; Predictive preventive personalized medicine (PPPM / 3P medicine); Prognostic assessment; SARS-CoV2; Targeted prevention.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to European Association for Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine (EPMA) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
COVID-19's Clinical-Pathological Evidence in Relation to Its Repercussion on the Central and Peripheral Nervous System.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1353:197-215. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-85113-2_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 35137375 Review.
-
Infections of the lung: a predictive, preventive and personalized perspective through the lens of evolution, the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 and its pathogenesis.EPMA J. 2020 Nov 13;11(4):581-601. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00230-1. eCollection 2020 Dec. EPMA J. 2020. PMID: 33204369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA and histone modifications as potent diagnostic and therapeutic targets to advance non-small cell lung cancer management from the perspective of 3P medicine.EPMA J. 2022 Nov 2;13(4):649-669. doi: 10.1007/s13167-022-00300-6. eCollection 2022 Dec. EPMA J. 2022. PMID: 36505890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implementing Personalized Medicine in COVID-19 in Andalusia: An Opportunity to Transform the Healthcare System.J Pers Med. 2021 May 26;11(6):475. doi: 10.3390/jpm11060475. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34073493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(19):1-43. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074489 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles of non-coding RNA derived from extracellular vesicles in regulating PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: insights into cancer immunotherapy and clinical applications.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 May 23;25(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03809-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40410719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long COVID as a Tauopathy: Of "Brain Fog" and "Fusogen Storms".Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 10;24(16):12648. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612648. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role and clinical applications of circular RNAs in human diseases.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Mar 28;25(1):77. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01575-4. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40148685 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: The Invisible Heroes and Villains of COVID-19 Central Neuropathology.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Mar;11(10):e2305554. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305554. Epub 2023 Dec 24. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38143270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiomics as instrument to promote 3P medical approaches for the overall management of respiratory syncytial viral infections.EPMA J. 2025 Jan 16;16(1):217-238. doi: 10.1007/s13167-024-00395-z. eCollection 2025 Mar. EPMA J. 2025. PMID: 39991100 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

