The Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Selective Oral Microbes, Antioxidant Activity and Preliminary Phytochemical Screening of Zingiber officinale
- PMID: 35668854
- PMCID: PMC9166953
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S364175
The Antimicrobial Efficacy Against Selective Oral Microbes, Antioxidant Activity and Preliminary Phytochemical Screening of Zingiber officinale
Abstract
Introduction: Ginger (Zingiber officinale) has been one of the most commonly consumed herbal medicines for a long time to treat several common diseases. Antibacterial activity, antioxidant properties and many bioactive compounds in ginger have been identified previously, which could be used as an alternative method to treat many infectious diseases.
Methods: The current study evaluates ginger's biochemical profile using qualitative and quantitative analysis and its bioactive potentials using antioxidant and antimicrobial assays against Streptococcus mutans and selective oral microbes. HPLC analysis was performed for the quantitative analysis. DPPH and disc diffusion assays were used for antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. The antimicrobial activity was checked against Streptococcus mutans, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus spp., and Lactobacillus spp. All solvents were removed by rotary evaporation before testing the dried extracts.
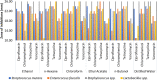
Results: The observed IC50 value showed that distilled water extract exhibited the highest antioxidant activity (43.9), followed by ethanol extract (52.4), and the lowest activity was observed in n-butanol extract (91.2) and n-hexane (90.6). Different plant extracts have shown significant antibacterial activity (p = 0.001) against each bacterium. The highest antibacterial activity against tested bacteria was observed in n-hexane, chloroform and ethanol extracts. In comparison, the ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water extracts showed low antibacterial activity.
Conclusion: This study emphasizes that Zingiber officinale (Z. officinale) against Gram-positive bacteria is an effective antimicrobial herb. Furthermore, it can be used as a potential natural source of antioxidants. Further studies on the toxicity analysis of ginger are recommended.
Keywords: Streptococcus mutans; dental; ginger; healthy food; herbal medicine; medicinal plants; oral microbes.
© 2022 Ahmed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The antioxidant activity, preliminary phytochemical screening of Zingiber zerumbet and antimicrobial efficacy against selective endodontic bacteria.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jun 1;11(8):4853-4860. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3462. eCollection 2023 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37576053 Free PMC article.
-
The antibacterial activity of nasturtium officinale extract on common oral pathogenic bacteria.Niger J Clin Pract. 2022 Sep;25(9):1466-1475. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_1887_21. Niger J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36149206
-
Assessment of the Phytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Potentials of Zingiber zerumbet.Molecules. 2023 Jan 3;28(1):409. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010409. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36615610 Free PMC article.
-
A critical review of Ginger's (Zingiber officinale) antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory activities.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 6;11:1364836. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1364836. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38903613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginger: A Nutraceutical Supplement for Protection Against Various Cardiovascular Diseases in Clinical Trials.Cureus. 2025 Mar 19;17(3):e80841. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80841. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40255738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the antidyslipidemic and nephroprotective effect of methanolic seed extract of Lepidium sativum on male Swiss albino mice fed on deep fried palm oil.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 11;12:1468704. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1468704. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40718006 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the push-out bond strength of AH Plus sealer to dentin after using different herbal irrigation solutions as the final rinse.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 2;17(11):e0276666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276666. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36322571 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and comparison of antibacterial efficacy of different concentrations of Chhattisgarh herbal product-Terminalia chebula fruit extract in opposition to Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro study.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Nov 29;12(2):1006-1011. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3814. eCollection 2024 Feb. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38370068 Free PMC article.
-
The antioxidant activity, preliminary phytochemical screening of Zingiber zerumbet and antimicrobial efficacy against selective endodontic bacteria.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jun 1;11(8):4853-4860. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3462. eCollection 2023 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37576053 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Therapy and Its Future Prospects for Ameliorating COVID-19: Clinical Applications, Efficacy, and Modality.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 4;11(7):1892. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071892. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khan M, Ullah N, Azhar M, Komal W, Muhammad W. A mini-review on the therapeutic potential of Zingiber officinale (ginger). Nat Prod. 2019;15:125.
-
- Wan-Nadilah WA, Hasima MN, Manaf AA. A review of medicinal plants and daily foods used in Southeast Asia possessing antidiabetic activity. J Agrobiotechnol. 2019;10:17–35.
-
- Munda S, Dutta S, Haldar S, Lal M. Chemical analysis and therapeutic uses of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) essential oil: a review. J Essent Oil-Bear Plants. 2018;21(4):994–1002. doi:10.1080/0972060X.2018.1524794 - DOI
-
- Mahboubi M. Zingiber officinale Rosc. essential oil, a review on its composition and bioactivity. Clin Phytoscience. 2019;5(1):1–12. doi:10.1186/s40816-018-0097-4 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous