Sources Identification and Health Risk Evaluation of 10 Heavy Metals (Metalloids) in Soils of the Aibi Lake Basin, Northwest China
- PMID: 35668868
- PMCID: PMC9166974
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8201972
Sources Identification and Health Risk Evaluation of 10 Heavy Metals (Metalloids) in Soils of the Aibi Lake Basin, Northwest China
Abstract
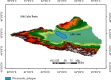
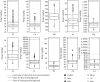
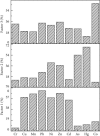
Recently, soils heavy metals pollution and health risks researches in oasis are few, and in this study, the Aibi lake basin-a typical oasis-was chosen as the research area, and then, we evaluated the pollution status and sources identification and analyzed the health risks of ten heavy metals in the soils. Results showed that (1) the average (range) values for As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn were (6.500-48.040) 20.011, (0.0002-0.088) 0.035, (0.060-18.150) 5.994, (24.160-106.400) 53.557, (3.460-58.760) 16.981, (0.0002-0.099) 0.042, (195.310-842.850) 483.311, (0.960-70.100) 14.235, (0.180-25.390) 8.086, and (22.340-156.250) 61.334 mg/kg, respectively, and we can get except for As, the maximum values of other nine elements all within the limited values provided by the soil environmental quality risk control standard of China. (2) Health risk evaluation showed that the total exposure amount for ADIing for children and adults was 0.001067998 and 0.000344707, ADIinh for children and adults was 9.69977E-08 and 7.95869E-08, ADIderm for children and adults was 8.52275E-06 and 2.09927E-06, and the order of exploring ways is ADIing > ADIinh > ADIderm. (3) The multivariate statistical analysis and PMF results showed that Cr, Cu, Co, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn primarily come from the natural background and man-made sources; Cd primarily comes from man-made sources; As and Hg come from natural background sources and industry sources. The results can provide reference values for heavy metals pollution prevention and the protection of the environment in the Aibi lake basin and as well as central Asia.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang Zhaoyong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Assessment of the distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the dry surface sediment of Aibi Lake in northwest China.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0120001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120001. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781032 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy metal pollution assessment, source identification, and health risk evaluation in Aibi Lake of northwest China.Environ Monit Assess. 2018 Jan 8;190(2):69. doi: 10.1007/s10661-017-6437-x. Environ Monit Assess. 2018. PMID: 29313160
-
Pollution assessment and health risks evaluation of (metalloid) heavy metals in urban street dust of 58 cities in China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jan;26(1):126-140. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3555-0. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30382518
-
Pollution status of heavy metals and metalloids in Chinese lakes: Distribution, bioaccumulation and risk assessment.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Dec 15;248:114293. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114293. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 36403301 Review.
-
A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years.J Environ Sci (China). 2021 Mar;101:217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.08.013. Epub 2020 Sep 3. J Environ Sci (China). 2021. PMID: 33334517 Review.
References
-
- Lin C. Q., Huang H. B., Hu G. R. Assessment of the speciation and pollution of heavy metals in paddy soils from the Jiulong River Basin. Environmental Science . 2019;40(1):453–460. In Chinese. - PubMed
-
- Lin H., Jin X. N., Luo M. K., Zhao Y. M. .Effects of bentonite on chemical forms and bioavailability of heavy metals in different types of farmland soils. Environmental Sciences . 2019;40(2):945–952. In Chinese. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

