Food safety and evaluation of intention to practice safe eating out measures during COVID-19: Cross sectional study in Indonesia and Malaysia
- PMID: 35668872
- PMCID: PMC9159731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.107920
Food safety and evaluation of intention to practice safe eating out measures during COVID-19: Cross sectional study in Indonesia and Malaysia
Abstract
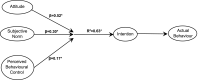
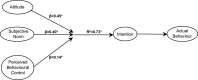
The COVID-19 pandemic has altered consumers' relationship with food, whether through shopping, increased home cooking, taking pre-cautionary measures during food shopping, food delivery and whilst dining out. This study aims to examine the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on consumers' food safety knowledge, attitude and practices and to identify the predictors of food safety practices during COVID-19. An online survey was conducted and received valid responses from 987 respondents. Data were analysed using descriptive statistics, non-parametric tests, Spearman's rho correlation and multiple regression. The Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) model was used to investigate the intention to practice safe eating out measures during COVID-19. The mean food safety knowledge score was 6.37 ± 1.37 (9.00 = highest score) of which 91.3% of total respondents from Indonesia and Malaysia scored ≥5 points. Consumers also demonstrated positive food safety attitude (4.06 ± 0.99) and reported high frequencies in conducting food safety practices (4.03 ± 0.82) during COVID-19. The TPB has provided valuable framework for understanding consumers' intention to practice safe eating out measures during COVID-19. The multiple regression model explained 63% and 73% of the variance in adherence to safe eating out practices in Indonesia and Malaysia and (p < 0.05) respectively. All the TPB antecedents i.e. attitude, subjective norms and perceived behavioural control were identified as significant predictors on consumers' eating out practices. This suggests that consumers with positive food safety attitude and strong family norms were more likely to adhere to safe eating out measures (e.g. selection of clean and less crowded restaurants, practicing hand hygiene, wearing masks and practising social distancing). The findings also suggest that to fully adhere to the safe practices, it is important to have sufficient support from restaurant staff to ensure social distancing and to provide adequate handwashing facilities. This is the first study to provide new empirical findings on consumers' intention to practice safe eating out measures during COVID-19.
Keywords: Eating out; Food safety; Handwashing; Social distancing; Theory of planned behaviour.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- BBC . BBC News; 2020. Coronavirus: Malaysian men in shopping muddle amid lockdown.https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/blogs-news-from-elsewhere-52040256 26 March. Available at:
-
- BBC Coronavirus beijing: Why an outbreak sparked a salmon panic in China. BBC news, 18 june. 2020. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-china-53089137 Available at:
-
- Bearth A., Cousin M.-E., Siegrist M. Poultry consumers' behaviour, risk perception and knowledge related to campylobacteriosis and domestic food safety. Food Control. 2014;44:166–176.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
