Hearing Loss Secondary to Systemic Sclerosis Vasculopathy: Case Study with a Short Review
- PMID: 35669089
- PMCID: PMC9166376
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S356818
Hearing Loss Secondary to Systemic Sclerosis Vasculopathy: Case Study with a Short Review
Abstract
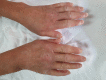
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a collagenosis with a substrate of chronic inflammation, which is determined by autoimmunity. The pathogenesis of this disease involves microvasculopathy (small vessel pathology) followed by excessive cutaneous and visceral fibrosis. Although acoustic and vestibular impairment is not classified as being a secondary pathology of SSc, several studies have identified cases of SSc that associate hearing loss and especially vertigo and tinnitus. This paper presents data from the medical literature that have identified vestibular and auditory symptoms among patients with SSc, associating the clinical case presentation of a patient suffering from SSc, which is associated with hearing loss. The need for additional studies on larger groups of patients is underlined, in order to clarify the impact of vasculopathy and fibrosis on the acoustic and vestibular analyzer in patients with SSc.
Keywords: capillaroscopy; fibrosis; hearing loss; systemic sclerosis; vasculopathy.
© 2022 Bobeica et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Barsotti S, Orlandi M, Codullo V, et al. One year in review 2019: systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37(Suppl119(4)):3–14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources