The Biological Functions and Clinical Significance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Corcern
- PMID: 35669924
- PMCID: PMC9163346
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.849217
The Biological Functions and Clinical Significance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Corcern
Abstract
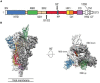
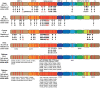
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is continuing to evolve, emerging novel variants with spike protein mutations. Although most mutations emerged in the SARS-CoV-2 genome are neutral or mildly deleterious, a small number of mutations can affect virus phenotype that confers the virus a fitness advantage. These mutations can enhance viral replication, raise the risk of reinfection and blunt the potency of neutralizing antibodies triggered by previous infection and vaccination. Since December 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 has emerged five quickly spreading strains, designated variants of concern (VOCs), including the Alpha (B.1.1.7) variant, the Beta (B.1.351) variant, the Gamma (P.1) variant, the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant and the Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant. These variants have a high number of the mutations in the spike protein that promotes viral cell entry through the angiotensin-converting enzyme -2 (ACE2). Mutations that have arisen in the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein are of great concern due to their potential to evade neutralizing antibodies triggered by previous infection and vaccines. The Alpha variant emerged in the United Kingdom in the second half of 2020 that has spread quickly globally and acquired the E484K mutation in the United Kingdom and the United States. The Beta and Gamma variants emerged in South Africa and Brazil, respectively, that have additional mutations at positions E484 and K417 in the RBD. SARS-CoV-2 variants containing the combination of N501Y, E484K, and K417N/T mutations exhibit remarkably decreased sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies mediated by vaccination or previous infection. The Gamma variant may result in more severe disease than other variants do even in convalescent individuals. The Delta variant emerged in India in December 2020 and has spread to many countries including the United States and the United Kingdom. The Delta variant has 8 mutations in the spike protein, some of which can influence immune responses to the key antigenic regions of RBD. In early November 2021, the Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant was first detected in Botswana and South Africa. The Omicron variant harbors more than 30 mutations in the spike protein, many of which are located within the RBD, which have been associated with increased transmissibility and immune evasion after previous infection and vaccination. Additionally, the Omicron variant contains 3 deletions and one insertion in the spike protein. Recently, the Omicron variant has been classified into three sublineages, including BA.1, BA.2, and BA.3, with strikingly different genetic characteristics. The Omicron BA.2 sublineage has different virological landscapes, such as transmissibility, pathogenicity and resistance to the vaccine-induced immunity compared to BA.1 and BA.3 sublineages. Mutations emerged in the RBD of the spike protein of VOCs increase viral replication, making the virus more infectious and more transmissible and enable the virus to evade vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibodies. Unfortunately, the emergence of novel SARS-CoV-2 VOCs has tempered early optimism regarding the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. This review addresses the biological and clinical significance of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs and their impact on neutralizing antibodies mediated by existing COVID-19 vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; the Alpha variant; the Beta variant; the Delta variant; the Gamma variant; the Omicron variant; variant of concern.
Copyright © 2022 Akkız.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19).2023 May 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 May 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 34033342 Free Books & Documents.
-
Pre-Omicron Vaccine Breakthrough Infection Induces Superior Cross-Neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 Compared to Infection Alone.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 12;23(14):7675. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147675. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887023 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling SARS-CoV-2 spike/ACE2 protein-protein interactions for predicting the binding affinity of new spike variants for ACE2, and novel ACE2 structurally related human protein targets, for COVID-19 handling in the 3PM context.EPMA J. 2022 Jan 6;13(1):149-175. doi: 10.1007/s13167-021-00267-w. eCollection 2022 Mar. EPMA J. 2022. PMID: 35013687 Free PMC article.
-
Immune evasion of neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023 Apr;70:13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.03.001. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023. PMID: 36948931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin, virological features, immune evasion and intervention of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 19;7(1):241. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01105-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35853878 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Occult Serologically Confirmed Cases of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus among the General Population in the Era of the Fourth Vaccination.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 22;13(16):4953. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164953. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39201097 Free PMC article.
-
Study of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Wild-Type and the Variants of Concern Real-Time Interactions with Monoclonal Antibodies and Convalescent Human Serum.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;13(8):784. doi: 10.3390/bios13080784. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622870 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Identification of Cross-Reacting IgG Hotspots to Predict Existing Immunity Evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Variants by a New Biotechnological Application of Phage Display.Viruses. 2023 Dec 29;16(1):58. doi: 10.3390/v16010058. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38257758 Free PMC article.
-
Designing multi-epitope based peptide vaccine targeting spike protein SARS-CoV-2 B1.1.529 (Omicron) variant using computational approaches.Struct Chem. 2022;33(6):2243-2260. doi: 10.1007/s11224-022-02027-6. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Struct Chem. 2022. PMID: 36160688 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and virological features of asymptomatic and mild symptomatic patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection at Shanghai Fangcang shelter hospital.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Sep;11(9):e1033. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1033. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37773703 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

