Radiomics quality score in renal masses: a systematic assessment on current literature
- PMID: 35671097
- PMCID: PMC10996962
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20211211
Radiomics quality score in renal masses: a systematic assessment on current literature
Abstract
Objective: To perform a systematic assessment and analyze the quality of radiomics methodology in current literature in the evaluation of renal masses using the Radiomics Quality Score (RQS) approach.
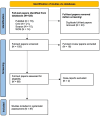
Methods: We systematically reviewed recent radiomics literature in renal masses published in PubMed, EMBASE, Elsevier, and Web of Science. Two reviewers blinded by each other's scores evaluated the quality of radiomics methodology in studies published from 2015 to August 2021 using the RQS approach. Owing to the diversity in the imaging modalities and radiomics applications, a meta-analysis could not be performed.
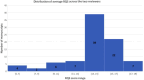
Results: Based on our inclusion/exclusion criteria, a total of 87 published studies were included in our study. The highest RQS was noted in three categories: reporting of clinical utility, gold standard, and feature reduction. The average RQS of the two reviewers ranged from 5 ≤ RQS≤19, with the maximum attainable RQS being 36. Very few (7/87 i.e., 8%) studies received an average RQS that ranged from 17 < RQS≤19, which represents studies with the highest RQS in our study. Many (39/87 i.e., 45%) studies received an average RQS that ranged from 13 < RQS≤15. No significant interreviewer scoring differences were observed.
Conclusions: We report that the overall scientific quality and reporting of radiomics studies in renal masses is suboptimal, and subsequent studies should bolster current deficiencies to improve reporting of radiomics methodologies.
Advances in knowledge: The RQS approach is a meaningful quantitative scoring system to assess radiomics methodology quality and supports a comprehensive evaluation of the radiomics approach before its incorporation into clinical practice.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluating the impact of the Radiomics Quality Score: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2025 Mar;35(3):1701-1713. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11341-y. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39794540 Free PMC article.
-
Post-radiotherapy stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer radiomics research: a systematic review and comparison of CLEAR and RQS frameworks.Eur Radiol. 2024 Oct;34(10):6527-6543. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10736-1. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38625613 Free PMC article.
-
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and megavoltage computed tomography (MVCT)-based radiomics in head and neck cancers: a systematic review and radiomics quality score assessment.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Sep 1;14(9):6963-6977. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-334. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39281127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality of science and reporting of radiomics in oncologic studies: room for improvement according to radiomics quality score and TRIPOD statement.Eur Radiol. 2020 Jan;30(1):523-536. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06360-z. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31350588
-
Evaluating the quality of radiomics-based studies for endometrial cancer using RQS and METRICS tools.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jan;35(1):202-214. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10947-6. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39014086 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pilot Study for the Assessment of the Best Radiomic Features for Bosniak Cyst Classification Using Phantom and Radiologist Inter-Observer Selection.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 10;13(8):1384. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13081384. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37189486 Free PMC article.
-
Renal MRI radiomics in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: a novel imaging approach for genotype identification.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Jun 15;20(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03841-x. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40518523 Free PMC article.

