Driving role of macrophages in transition from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 35671177
- PMCID: PMC9276339
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002100
Driving role of macrophages in transition from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease
Abstract
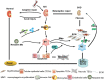
Acute kidney injury (AKI), characterized by acute renal dysfunction, is an increasingly common clinical problem and an important risk factor in the subsequent development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Regardless of the initial insults, the progression of CKD after AKI involves multiple types of cells, including renal resident cells and immune cells such as macrophages. Recently, the involvements of macrophages in AKI-to-CKD transition have garnered significant attention. Furthermore, substantial progress has also been made in elucidating the pathophysiological functions of macrophages from the acute kidney to repair or fibrosis. In this review, we highlight current knowledge regarding the roles and mechanisms of macrophage activation and phenotypic polarization, and transdifferentiation in the development of AKI-to-CKD transition. In addition, the potential of macrophage-based therapy for preventing AKI-to-CKD transition is also discussed.
Copyright © 2022 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Y. Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int 2006; 69:213–217. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

