The Role of Viral RNA Degrading Factors in Shutoff of Host Gene Expression
- PMID: 35671567
- PMCID: PMC9530000
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-virology-100120-012345
The Role of Viral RNA Degrading Factors in Shutoff of Host Gene Expression
Abstract
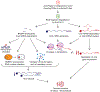
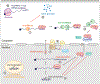
Many viruses induce shutoff of host gene expression (host shutoff) as a strategy to take over cellular machinery and evade host immunity. Without host shutoff activity, these viruses generally replicate poorly in vivo, attesting to the importance of this antiviral strategy. In this review, we discuss one particularly advantageous way for viruses to induce host shutoff: triggering widespread host messenger RNA (mRNA) decay. Viruses can trigger increased mRNA destruction either directly, by encoding RNA cleaving or decapping enzymes, or indirectly, by activating cellular RNA degradation pathways. We review what is known about the mechanism of action of several viral RNA degradation factors. We then discuss the consequences of widespread RNA degradation on host gene expression and on the mechanisms of immune evasion, highlighting open questions. Answering these questions is critical to understanding how viral RNA degradation factors regulate host gene expression and how this process helps viruses evade host responses and replicate.
Keywords: RNA decay; decapping enzymes; host shutoff; ribonuclease; virus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanisms and consequences of mRNA destabilization during viral infections.Virol J. 2024 Feb 6;21(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02305-1. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38321453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feline Calicivirus Proteinase-Polymerase Protein Degrades mRNAs To Inhibit Host Gene Expression.J Virol. 2021 Jun 10;95(13):e0033621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00336-21. Epub 2021 Jun 10. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33853967 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza A Virus Protein PA-X Contributes to Viral Growth and Suppression of the Host Antiviral and Immune Responses.J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(12):6442-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00319-15. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25855745 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles for RNA degradation in viral replication and antiviral defense.Virology. 2015 May;479-480:600-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25721579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host Shutoff in Influenza A Virus: Many Means to an End.Viruses. 2018 Sep 5;10(9):475. doi: 10.3390/v10090475. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30189604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Invasion by exogenous RNA: cellular defense strategies and implications for RNA inference.Mar Life Sci Technol. 2023 Nov 24;5(4):573-584. doi: 10.1007/s42995-023-00209-7. eCollection 2023 Nov. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 38045546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infectious bursal disease virus VP5 triggers host shutoff in a transcription-dependent manner.mBio. 2024 Mar 13;15(3):e0343323. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03433-23. Epub 2024 Jan 30. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38289089 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus takeover of host cell translation and intracellular antiviral response: a molecular perspective.EMBO J. 2024 Jan;43(2):151-167. doi: 10.1038/s44318-023-00019-8. Epub 2024 Jan 10. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38200146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How influenza shuts down host transcription.Nat Microbiol. 2023 Jul;8(7):1195-1196. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01416-9. Nat Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37349589 No abstract available.
-
Mechanisms and consequences of mRNA destabilization during viral infections.Virol J. 2024 Feb 6;21(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02305-1. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38321453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

