Adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35671640
- PMCID: PMC9148928
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108906
Adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: High speed of COVID-19 vaccination has raised some concerns about the safety of the new vaccines. It is of a great importance to perform a review of the safety and efficacy of the COVID-19 vaccines.
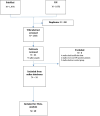
Methods: Two International electronic databases (PubMed, ISI) were searched for clinical trials reporting efficacy and safety of COVID-19 vaccines compared to control group. Pooled risk ratio (RR) for total, systemic and local adverse events following immunization was calculated for different vaccine modalities.
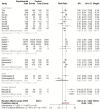
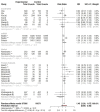
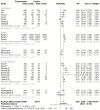
Results: The pooled RRs of total adverse reactions for Inactivated, mRNA, and vector vaccines were 1.46 (95% CI: 1.19-1.78), 2.01 (95% CI: 1.82 - 2.23), and 1.65 (95% CI: 1.31 - 2.32) respectively. The pooled RR for occurrence of systemic adverse reactions following immunization for different vaccine modalities was 1.13 (95% CI: 0.79 - 1.61), 1.53 (95% CI 1.08 - 2.16), 1.58 (95% CI: 1.13 - 1.90), 0.72 (95% CI: 0.34 - 1.55), and 1.62 (95% CI: 1.39 - 1.89) for inactivated vaccine, mRNA, vector, DNA, and protein subunit vaccines respectively. The pooled RR of local adverse event following immunization with inactivated vaccine, mRNA vaccine, vector vaccine, DNA vaccine, and protein subunit vaccine was 2.18 (95% CI: 1.32 - 3.59), 4.96 (95% CI: 4.02 - 6.11), 1.48 (95% CI: 0.88-2.50) 1.04 (95% CI: 0.12-8.75), and 4.09 (95% CI: 2.63-6.35) respectively.
Conclusion: mRNA vaccines are associated with greater risk of adverse events following immunization. However, at the present moment the benefits of all types of vaccines approved by WHO, still outweigh the risks of them and vaccination if available, is highly recommended.
Keywords: Adverse events; COVID-19; Efficacy; SARS-CoV-2; Safety.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological update—9 March 2021.https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update---.... Accessed 15 Mar 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

