COL1A1 and FGFR2 Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Found in Class II and Class III Skeletal Malocclusions in Javanese Population
- PMID: 35672017
- PMCID: PMC9949934
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1744371
COL1A1 and FGFR2 Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Found in Class II and Class III Skeletal Malocclusions in Javanese Population
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this article is to analyze and compare the presence of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of COL1A1 and FGFR2 in class II and class III Javanese populations.
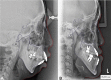
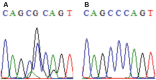
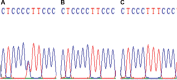
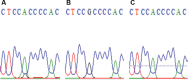
Materials and methods: Cephalometric radiographs from total 63 patients of class II and III were analyzed. SNP analysis was performed based on both COL1A1 and FGFR2 sequences amplified from total DNA of patients' fresh blood. Principal component analysis was done to calculate the data and find the correlation of the cephalometric indicators influenced by each mutation. t-test and Mann-Whitney analysis were performed to check the significance of differences occurred in each studied parameter (p < 0.05).
Result: There were three COL1A1 SNPs found in class II and only two in class III, while three FGFR2 SNPs found in both classes. Class II phenotype seemed to be strongly influenced by Y-axis and mandibular plane angle, while class III by lower gonial angle and mandibular plane angle.
Conclusion: Based on this study, we suggest that rs2249492 of COL1A1 and rs2981582 of FGFR2 play important roles in class III, while rs2277632 of COL1A1 and rs2981582 of FGFR2 play important role in class II skeletal malocclusion in Javanese population.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) of COL1A1 and COL11A1 in Class II Skeletal Malocclusion of Ethnic Javanese Patient.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2020 Apr 24;12:173-179. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S247729. eCollection 2020. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2020. PMID: 32425611 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate Gene Analyses of Skeletal Variation in Malocclusion.J Dent Res. 2015 Jul;94(7):913-20. doi: 10.1177/0022034515581643. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25910506 Free PMC article.
-
Cephalometric Characteristic of Skeletal Class II Malocclusion in Javanese Population at Universitas Airlangga Dental Hospital.Contemp Clin Dent. 2018 Sep;9(Suppl 2):S342-S346. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_465_18. Contemp Clin Dent. 2018. PMID: 30294169 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Polymorphisms in FGFR2 Underlie Skeletal Malocclusion.J Dent Res. 2019 Nov;98(12):1340-1347. doi: 10.1177/0022034519872951. Epub 2019 Sep 11. J Dent Res. 2019. PMID: 31509720
-
Vertical Cephalometric Characteristics in Class III Malocclusions.Curr Health Sci J. 2022 Oct-Dec;48(4):446-453. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.48.04.12. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Curr Health Sci J. 2022. PMID: 37304795 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) genetic polymorphisms contribute to fused roots in human molars.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 10;20(4):e0316904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316904. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40208883 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the COL1A1 Gene Polymorphisms on Pain Perception in Tennis Elbow Patients: A Two-Year Prospective Cohort Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 9;25(23):13221. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313221. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Doraczynska-Kowalik A, Nelke K H, Pawlak W, Sasiadek M M, Gerber H. Genetic factors involved in mandibular prognathism. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(05):e422–e431. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Wu C, Lin J, Shao J, Chen Q, Luo E. Genetic etiology in nonsyndromic mandibular prognathism. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(01):161–169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

