Prenatal hypoxia alters the early ontogeny of dopamine neurons
- PMID: 35672280
- PMCID: PMC9174174
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-022-02005-w
Prenatal hypoxia alters the early ontogeny of dopamine neurons
Abstract
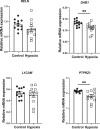
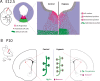
Dopaminergic (DA) dysfunction is a significant feature in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Established developmental risk factors for schizophrenia such as maternal immune activation (MIA) or developmental vitamin D (DVD) deficiency, when modelled in animals, reveal the differentiation of early DA neurons in foetal brains is delayed suggesting this may be a convergent aetiological pathway. Here we have assessed the effects of prenatal hypoxia, another well-known developmental risk factor for schizophrenia, on developing DA systems. Pregnant mice were exposed to a hypoxic environment of 10% oxygen for 48 h from embryonic day 10 (E10) to E12. Embryonic brains were collected and the positioning of mesencephalic cells, expression of DA specification and maturation factors were examined along with the expression of factors that may govern the migration of these neurons. We show that prenatal hypoxia results in a decrease in dopaminergic progenitors retards early DA neuron lateral migration and reduces expression of the receptors known to govern this process. A second time-point, postnatal day 10 (P10) was also examined in order to assess whether prenatal hypoxia alters early presynaptic architecture in the developing striatum. We show reduced expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in the postnatal striatum along with increases in the density of high-probability DA release sites within TH varicosities. These findings add to the emerging literature showing that multiple epidemiologically validated environmental risk factors for schizophrenia may induce early alterations to develop DA systems. This may represent a possible convergent mechanism in the onset of presynaptic DA dysfunction in patients.
© 2022. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

