Enhanced BRAF engagement by NRAS mutants capable of promoting melanoma initiation
- PMID: 35672316
- PMCID: PMC9174180
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30881-9
Enhanced BRAF engagement by NRAS mutants capable of promoting melanoma initiation
Abstract
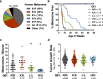
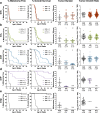
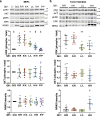
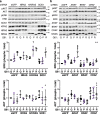
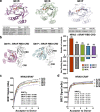
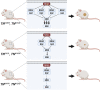
A distinct profile of NRAS mutants is observed in each tumor type. It is unclear whether these profiles are determined by mutagenic events or functional differences between NRAS oncoproteins. Here, we establish functional hallmarks of NRAS mutants enriched in human melanoma. We generate eight conditional, knock-in mouse models and show that rare melanoma mutants (NRAS G12D, G13D, G13R, Q61H, and Q61P) are poor drivers of spontaneous melanoma formation, whereas common melanoma mutants (NRAS Q61R, Q61K, or Q61L) induce rapid tumor onset with high penetrance. Molecular dynamics simulations, combined with cell-based protein-protein interaction studies, reveal that melanomagenic NRAS mutants form intramolecular contacts that enhance BRAF binding affinity, BRAF-CRAF heterodimer formation, and MAPK > ERK signaling. Along with the allelic series of conditional mouse models we describe, these results establish a mechanistic basis for the enrichment of specific NRAS mutants in human melanoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.E.B. and B.M.M. are inventors of TN61 cell lines licensed to Millipore. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hobbs GA, et al. Atypical KRASG12R mutant is impaired in PI3K signaling and macropinocytosis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:104–123. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

