DoE-derived continuous and robust process for manufacturing of pharmaceutical-grade wide-range LNPs for RNA-vaccine/drug delivery
- PMID: 35672337
- PMCID: PMC9172984
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12100-z
DoE-derived continuous and robust process for manufacturing of pharmaceutical-grade wide-range LNPs for RNA-vaccine/drug delivery
Abstract
Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology has become extremely demanding for delivering RNA-products and other drugs. However, there is no platform to manufacture pharmaceutical-grade LNPs with desired particle size from a wide range in continuous mode. We have developed a unique platform to obtain any specific size-range of LNPs from 60 to 180 nm satisfying pharmaceutical regulatory requirements for polydispersity index, sterility, dose uniformity and bio-functionality. We applied design of experiment (DoE) methodology and identified the critical process parameters to establish the process for global application. Cross-point validation within the response map of DoE confirmed that the platform is robust to produce specific size (± 10 nm) of LNPs within the design-range. The technology is successfully transformed to production scale and validated. Products from R&D, pilot and production batches for a candidate SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-vaccine generated equivalent biological responses. The data collectively established the robustness and bio-uniformity of doses for global RNA-vaccine/drug formulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

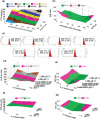
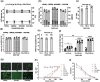
Similar articles
-
Lipid nanoparticle formulations for optimal RNA-based topical delivery to murine airways.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022 Sep 1;176:106234. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106234. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35688311
-
Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Jan 4;55(1):2-12. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00544. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 34850635 Review.
-
Throughput-scalable manufacturing of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccines.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 15;120(33):e2303567120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2303567120. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37556502 Free PMC article.
-
Polydispersity characterization of lipid nanoparticles for siRNA delivery using multiple detection size-exclusion chromatography.Anal Chem. 2012 Jul 17;84(14):6088-96. doi: 10.1021/ac3007768. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22816783
-
Microfluidic production of mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles for vaccine applications.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022 Oct;19(10):1381-1395. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2022.2135502. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 36223174 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning-driven optimization of mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine quality with XGBoost/Bayesian method and ensemble model approaches.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Nov;14(11):100996. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.100996. Epub 2024 May 8. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39759971 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Micromixer Design on Lipid Nanocarriers Manufacturing for the Delivery of Proteins and Nucleic Acids.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 7;16(4):507. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040507. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675169 Free PMC article.
-
Quality by Design (QbD) and Design of Experiments (DOE) as a Strategy for Tuning Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations for RNA Delivery.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 11;11(10):2752. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102752. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality by design for mRNA platform purification based on continuous oligo-dT chromatography.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Sep 11;35(4):102333. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102333. eCollection 2024 Dec 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39380714 Free PMC article.
-
Platform Technology in Global Vaccine Regulation: Development, Applications, and Regulatory Strategies with Insights from China.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;12(12):1436. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121436. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pascolo S. Vaccination with messenger RNA. Methods Mol. Med. 2006;127:23–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

