Network pharmacology and experimental verification based research into the effect and mechanism of Aucklandiae Radix-Amomi Fructus against gastric cancer
- PMID: 35672352
- PMCID: PMC9174187
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13223-z
Network pharmacology and experimental verification based research into the effect and mechanism of Aucklandiae Radix-Amomi Fructus against gastric cancer
Abstract
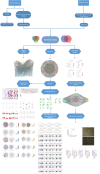
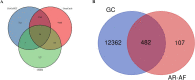
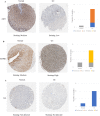
To investigate the mechanism of the Aucklandiae Radix-Amomi Fructus (AR-AF) herb pair in treating gastric cancer (GC) by using network pharmacology and experimental verification. Using the traditional Chinese medicine system pharmacology database and analysis platform (TCMSP), the major active components and their corresponding targets were estimated and screened out. Using Cytoscape 3.7.2 software, a visual network was established using the active components of AR-AF and the targets of GC. Based on STRING online database, the protein interaction network of vital targets was built and analyzed. With the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) server, the gene ontology (GO) biological processes and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signaling pathways of the target enrichment were performed. AutoDock Vina was used to perform molecular docking and calculate the binding affinity. The mRNA and protein expression levels of the hub targets were analyzed by the Oncomine, GEPIA, HPA databases and TIMER online tool, and the predicted targets were verified by qRT-PCR in vitro. Eremanthin, cynaropicrin, and aceteugenol were identified as vital active compounds, and AKT1, MAPK3, IL6, MAPK1, as well as EGFR were considered as the major targets. These targets exerted therapeutic effects on GC by regulating the cAMP signaling pathway, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Molecular docking revealed that these active compounds and targets showed good binding interactions. The validation in different databases showed that most of the results were consistent with this paper. The experimental results confirmed that eremanthin could inhibit the proliferation of AGS by reducing the mRNA expression of hub targets. As predicted by network pharmacology and validated by the experimental results, AR-AF exerts antitumor effects through multiple components, targets, and pathways, thereby providing novel ideas and clues for the development of preparations and the treatment of GC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





















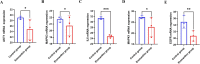
References
-
- Le X, Mu J, Peng W, Tang J, Xiang Q, Tian S, Feng Y, He S, Qiu Z, Ren G, et al. DNA methylation downregulated ZDHHC1 suppresses tumor growth by altering cellular metabolism and inducing oxidative/ER stress-mediated apoptosis and pyroptosis. Theranostics. 2020;10(21):9495–9511. doi: 10.7150/thno.45631. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

