Significant increase in azithromycin "resistance" and susceptibility to ceftriaxone and cefixime in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in 26 European countries, 2019
- PMID: 35672671
- PMCID: PMC9171984
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07509-w
Significant increase in azithromycin "resistance" and susceptibility to ceftriaxone and cefixime in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in 26 European countries, 2019
Abstract
Background: The European Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Programme (Euro-GASP) performs annual sentinel surveillance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae susceptibility to therapeutically relevant antimicrobials across the European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA). We present the Euro-GASP results from 2019 (26 countries), linked to patient epidemiological data, and compared with data from previous years.
Methods: Agar dilution and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) gradient strip methodologies were used to determine the antimicrobial susceptibility (using EUCAST clinical breakpoints, where available) of 3239 N. gonorrhoeae isolates from 26 countries across the EU/EEA. Significance of differences compared with Euro-GASP results in previous years was analysed using Z-test and the Pearson's χ2 test was used to assess significance of odds ratios for associations between patient epidemiological data and antimicrobial resistance.
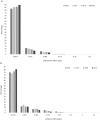
Results: European N. gonorrhoeae isolates collected between 2016 and 2019 displayed shifting MIC distributions for; ceftriaxone, with highly susceptible isolates increasing over time and occasional resistant isolates each year; cefixime, with highly-susceptible isolates becoming increasingly common; azithromycin, with a shift away from lower MICs towards higher MICs above the EUCAST epidemiological cut-off (ECOFF); and ciprofloxacin which is displaying a similar shift in MICs as observed for azithromycin. In 2019, two isolates displayed ceftriaxone resistance, but both isolates had MICs below the azithromycin ECOFF. Cefixime resistance (0.8%) was associated with patient sex, with resistance higher in females compared with male heterosexuals and men-who-have-sex-with-men (MSM). The number of countries reporting isolates with azithromycin MICs above the ECOFF increased from 76.9% (20/26) in 2016 to 92.3% (24/26) in 2019. Isolates with azithromycin MICs above the ECOFF (9.0%) were associated with pharyngeal infection sites. Following multivariable analysis, ciprofloxacin resistance remained associated with isolates from MSM and heterosexual males compared with females, the absence of a concurrent chlamydial infection, pharyngeal infection sites and patients ≥ 25 years of age.
Conclusions: Resistance to ceftriaxone and cefixime remained uncommon in EU/EEA countries in 2019 with a significant decrease in cefixime resistance observed between 2016 and 2019. The significant increase in azithromycin "resistance" (azithromycin MICs above the ECOFF) threatens the effectiveness of the dual therapy (ceftriaxone + azithromycin), i.e., for ceftriaxone-resistant cases, currently recommended in many countries internationally and requires close monitoring.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Azithromycin; Ceftriaxone; Europe; European Economic Area (EEA); European Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Programme (Euro-GASP); European Union (EU); Gonorrhoea; Surveillance; Treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Eyre DW, Sanderson ND, Lord E, Regisford-Reimmer N, Chau K, Barker L, et al. Gonorrhoea treatment failure caused by a Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain with combined ceftriaxone and high-level azithromycin resistance, England, February 2018. Eurosurveillance. 2018;23(27).
-
- Morita-Ishihara T, Unemo M, Furubayashi K, Kawahata T, Shimuta K, Nakayama S, et al. Treatment failure with 2 g of azithromycin (extended-release formulation) in gonorrhoea in Japan caused by the international multidrug-resistant ST1407 strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69(8):2086–2090. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku118. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Poncin T, Fouere S, Braille A, Camelena F, Agsous M, Bebear C, et al. Multidrug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae failing treatment with ceftriaxone and doxycycline in France, November 2017. Eurosurveillance. 2018;23(21).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

