The role of YAP1 in liver cancer stem cells: proven and potential mechanisms
- PMID: 35672802
- PMCID: PMC9171972
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-022-00387-z
The role of YAP1 in liver cancer stem cells: proven and potential mechanisms
Abstract
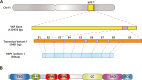
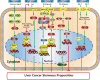
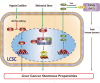
YAP1 (Yes-associated protein 1) is one of the principal factors that mediates oncogenesis by acting as a driver of gene expression. It has been confirmed to play an important role in organ volume control, stem cell function, tissue regeneration, tumorigenesis and tumor metastasis. Recent research findings show that YAP1 is correlated with the stemness of liver cancer stem cells, and liver cancer stem cells are closely associated with YAP1-induced tumor initiation and progression. This article reviews the advancements made in research on the mechanisms by which YAP1 promotes liver cancer stem cells and discusses some potential mechanisms that require further study.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest related to this manuscript. The contents of this manuscript have been approved by all authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ovatodiolide suppresses yes-associated protein 1-modulated cancer stem cell phenotypes in highly malignant hepatocellular carcinoma and sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy in vitro.Toxicol In Vitro. 2018 Sep;51:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Toxicol In Vitro. 2018. PMID: 29698666
-
lncRNA MALAT1 modulates cancer stem cell properties of liver cancer cells by regulating YAP1 expression via miR‑375 sponging.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Aug;22(2):1449-1457. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11196. Epub 2020 May 29. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32626943 Free PMC article.
-
YAP1 affects the prognosis through the regulation of stemness in endometrial cancer.PeerJ. 2023 Sep 20;11:e15891. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15891. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37744228 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the VEGF-C/VEGFR3 axis suppresses Slug-mediated cancer metastasis and stemness via inhibition of KRAS/YAP1 signaling.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 17;8(3):5603-5618. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13629. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27901498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hippo Pathway as Drug Targets in Cancer Therapy and Regenerative Medicine.Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(4):447-454. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160112115641. Curr Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 26758663 Review.
Cited by
-
USP24 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by deubiquitinating and stabilizing YAP1.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Apr 26;25(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03796-w. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40287768 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Stem Cell and Hepatic Stellate Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231163677. doi: 10.1177/15330338231163677. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36938618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A covalent inhibitor of the YAP-TEAD transcriptional complex identified by high-throughput screening.RSC Chem Biol. 2023 Aug 29;4(11):894-905. doi: 10.1039/d3cb00044c. eCollection 2023 Nov 1. RSC Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37920398 Free PMC article.
-
Nutraceutical Evaluation of Trigonelline's Therapeutic Potential by Targeting Bladder Cancer Stem Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts via Downregulation of TGFβ3/GLI2/YAP1 Signaling Hub.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Feb 18;22(5):1194-1207. doi: 10.7150/ijms.107228. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40027190 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signaling in Ehrlichia infection and cancer: Parallels in pathogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Feb 14;15:1539847. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1539847. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40028182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391(10127):1301–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

