Current advances and future perspectives on the functional roles and clinical implications of circular RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: more influential than expected
- PMID: 35672804
- PMCID: PMC9171998
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-022-00388-y
Current advances and future perspectives on the functional roles and clinical implications of circular RNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: more influential than expected
Abstract
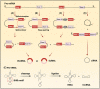
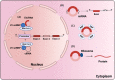
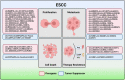
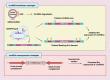
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most aggressive gastrointestinal cancers with high incidence and mortality. Therefore, it is necessary to identify novel sensitive and specific biomarkers for ESCC detection and treatment. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a type of noncoding RNAs featured by their covalently closed circular structure. This special structure makes circRNAs more stable in mammalian cells, coupled with their great abundance and tissue specificity, suggesting circRNAs may present enormous potential to be explored as valuable prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers for tumor. Mounting studies verified the critical roles of circRNAs in regulating ESCC cells malignant behaviors. Here, we summarized the current progresses in a handful of aberrantly expressed circRNAs, and elucidated their biological function and clinical significance in ESCC, and introduced a series of databases for circRNA research. With the improved advancement in high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics technique, new frontiers of circRNAs will pave the path for the development of precision treatment in ESCC.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Esophageal squamous carcinoma (ESCC); Treatment; circRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cocquerelle C, Mascrez B, Hetuin D, Bailleul B. Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J. 1993;7(1):155–60. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

