Measurement of Phacoemulsification Vacuum Pressure in the Oertli CataRhex3
- PMID: 35673346
- PMCID: PMC9167595
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S356657
Measurement of Phacoemulsification Vacuum Pressure in the Oertli CataRhex3
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the actual vacuum pressure generated by the Oertli CataRhex 3® (Oertli), using an external measuring system.
Methods: The effective vacuum pressure created by the Oertli was measured with a pressure device that was continuous with the vacuum tubing system while closed to the external environment. Measurements were taken with the machine set to 300 and 500 mmHg at flow rates of 20, 35, and 50 mL/min and at bottle heights of 60, 80, and 100 cm. Pressures were recorded after the foot pedal was depressed to vacuum setting (second position), and the pressure was allowed to stabilize. Subsequently, it was compared to the pressure value displayed by the machine.
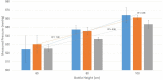
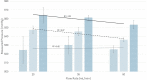
Results: Externally measured vacuum pressure was on average 13.02% greater (39.05 mmHg) than displayed vacuum pressure at 300 mmHg (P < 0.005) and 8.60% greater (42.98 mmHg) than displayed vacuum at 500 mmHg (P < 0.005). The average difference between displayed and measured pressure increased with increasing bottle heights.
Conclusion: On average, the vacuum pressure generated in the Oertli was found to be significantly higher than the machine's reading when the machine was set at 300 mmHg and 500 mmHg. Adjusting vacuum had variable effects on the measured versus displayed pressure readings.
Keywords: Oertli CataRhex 3; bottle height; flow rate; phacoemulsification; vacuum pressure.
© 2022 Peterson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Randall J Olson is on the Board of Directors of Perceive Bio and the Scientific Advisory Board of Perfect Lens. Dr. Jeff H Pettey reports a consulting agreement for Lensar, outside the submitted work. The other authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Zanini M, Savini G, Buratto L. Physical principles of phacoemulsification. In: Buratto L, Werner L, Zanini M, Apple DJ, editors. Phacoemulsification: Principles and Techniques. 2nd ed. Thorofare, NJ: Slack, Inc.; 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

