Calotropin and corotoxigenin 3-O-glucopyranoside from the desert milkweed Asclepias subulata inhibit the Na+/K+-ATPase activity
- PMID: 35673388
- PMCID: PMC9167584
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13524
Calotropin and corotoxigenin 3-O-glucopyranoside from the desert milkweed Asclepias subulata inhibit the Na+/K+-ATPase activity
Abstract
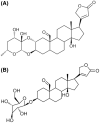
Na+/K+-ATPase is an essential transmembrane enzyme found in all mammalian cells with critical functions for cell ion homeostasis. The inhibition of this enzyme by several cardiotonic steroids (CTS) has been associated with the cytotoxic effect on cancer cell lines of phytochemicals such as ouabain and digitoxin. This study evaluated the inhibitory capacity of cardenolides calotropin and corotoxigenin 3-O-glucopyranoside (C3OG) from Asclepias subulata over the Na+/K+-ATPase activity in vitro and silico. The inhibitory assays showed that calotropin and C3OG decreased the Na+/K+-ATPase activity with IC50 values of 0.27 and 0.87 μM, respectively. Furthermore, the molecules presented an uncompetitive inhibition on Na+/K+-ATPase activity, with Ki values of 0.2 μM to calotropin and 0.5 μM to C3OG. Furthermore, the molecular modeling indicated that calotropin and C3OG might interact with the Thr797 and Gln111 residues, considered essential to the interaction with the Na+/K+-ATPase. Besides, these cardenolides can interact with amino acid residues such as Phe783, Leu125, and Ala323, to establish hydrophobic interactions on the binding site. Considering the results, these provide novel evidence about the mechanism of action of cardenolides from A. subulata, proposing that C3OG is a novel cardenolide that deserves further consideration for in vitro cellular antiproliferative assays and in vivo studies as an anticancer molecule.
Keywords: ATPase activity; Asclepias subulata; Cardenolides; Uncompetitive inhibition.
© 2022 Meneses-Sagrero et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Rogerio R. Sotelo-Mundo is an Academic Editor for PeerJ.
Figures







Similar articles
-
An updated pharmacological insight into calotropin as a potential therapeutic agent in cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1160616. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1160616. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37138852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic activities of cardenolide glycosides from Asclepias subulata.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 4;193:303-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27545974
-
Antiproliferative activity of cardenolide glycosides from Asclepias subulata.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Aug 2;171:280-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.05.057. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26068432
-
Antiproliferative activity of standardized herbal phytopreparation from Asclepias subulata.F1000Res. 2022 May 16;11:527. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.111181.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2022. PMID: 37025948 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides: their roles in hypertension, salt metabolism, and cell growth.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):C509-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00098.2007. Epub 2007 May 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17494630 Review.
Cited by
-
An updated pharmacological insight into calotropin as a potential therapeutic agent in cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1160616. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1160616. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37138852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pump, the exchanger, and the Holy Spirit: tracing the 40-year evolution of the Ouabain-Na+ pump endocrine system concept.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 May 30;87(7):4281-4302. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003438. eCollection 2025 Jul. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40851957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Na+/K+-ATPase: More than an Electrogenic Pump.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 1;25(11):6122. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116122. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Structures, Spectrometric Quantification, and Inhibitory Properties of Cardenolides from Asclepias curassavica Seeds.Molecules. 2022 Dec 23;28(1):105. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010105. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal AA, Boroczky K, Haribal M, Hastings AP, White RA, Jiang RW, Duplais C. Cardenolides, toxicity and the costs of sequestration in the coevolutionary interaction between monarchs and milkweeds. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America. 2021;118(16):1–18. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2024463118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Snafi AE. The pharmacological and toxicological effects of Coronilla varia and Coronilla scorpioides: A review. The Pharmaceutical and Chemical Journal. 2016;3(2):105–114.
-
- Azalim P, do Monte FM, Rendeiro MM, Liu X, O’ Doherty GA, Fontes CF, Guimaraes-Leitao S, Quintas LFM, Noel F. Conformational states of the pig kidney Na+/K+-ATPase differently affect bufadienolides and cardenolides: a direct structure-activity and structure-kinetics study. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2020;17(113679):1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113679. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bai Y, Zhu W, Xu Y, Xie Z, Akihisa T, Manosroi J, Sun H, Feng F, Liu W, Zhang J. Characterization, quantification, similarity evaluation and combination with Na+/K+-ATPase of cardiac glycosides from Streblus asper. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2019;87:265–275. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.03.049. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

