Pharmacogenomics of sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetes mellitus; a systematic review
- PMID: 35673432
- PMCID: PMC9167353
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-021-00908-x
Pharmacogenomics of sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetes mellitus; a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: Genetic factors have a role in response to a target medication (personalized medicine). This study aimed to review available evidence about the relationship between gene variants and therapeutic response to sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetes, systematically.
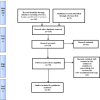
Methods: An extensive search was done in Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science with specific search strategy in the field from the beginning until the 1st of Jan. 2021. After sending records to endnote software and removing duplicate records remained documents were screened by title and abstract. Full texts of remained documents were assessed after removing un-related records. Required data was extracted from remained documents and records were categorized according to gene/SNP studied.
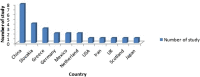
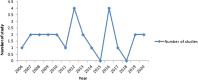
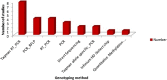
Results: Finally, 26 studies with 9170 T2DM patients with a mean age of 59.47 ± 6.67 (49.7-75.2 years) remained. The most contribution was from China, Slovakia and Greece, respectively and the most genes studied were CYP2C9, KCNJ11, and both KCNQ1 and ABCC8 with 10, 7, and 4 articles, respectively. Also, rs1799853 and rs1057910 (each with seven studies), rs5219 with six studies and CYP2C9*1(with four articles), respectively were the most common variants investigated. Studies about each gene obtained different positive or negative results and were not consistent.
Conclusion: Considering heterogeneity between SFUs pharmacogenomic studies regarding the method, sample size, population, gene/variant studied, and outcome and findings, these studies are not conclusive and need further studies.
Keywords: Diabetes; Personalized medicine; Pharmacogenomics; Polymorphism; Sulfonylurea; Variant.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 2019: Brussels; Belgium.
-
- Ma Q, Lu AY. Pharmacogenetics, pharmacogenomics, and individualized medicine. Pharmacol Rev. 2011;63:437–459. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

